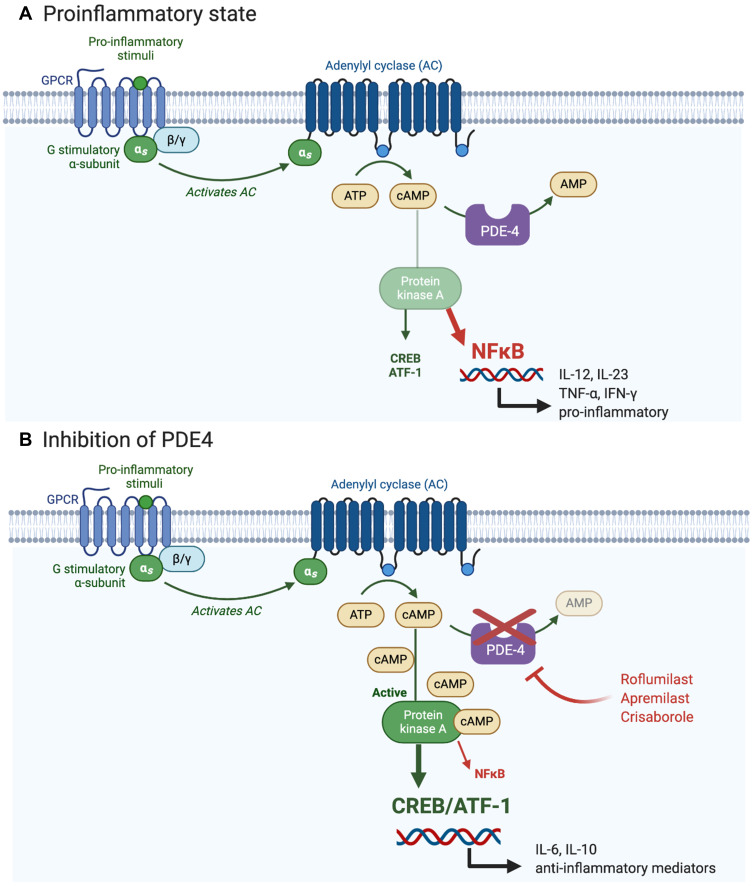
Figure 1.
Overview of the PDE4/PKA cascade pathway. Panel (A). In a proinflammatory state, PDE-4 promotes production of inflammatory cytokines through activation of NFκB and reduces production of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 by degrading cAMP which is responsible for maintaining immune homeostasis. Panel (B). Inhibition of PDE4 leads to elevation of cAMP which triggers the PKA pathway. PKA suppresses the production of proinflammatory mediators and promotes the production of anti-inflammatory mediators, such as IL-10, through gene transcription driven by CREB and ATF-1.
Notes: Adapted from “Activation of Protein Kinase A (PKA)”, by BioRender.com (2020). Retrieved from https://app.biorender.com/biorender-templates.
Abbreviations: ATF-1, cAMP-dependent transcription factor 1; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CREB, cAMP response element binding protein; IL, interleukin; PDE-4, phosphodiesterase-4; PKA, protein kinase A; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa B.