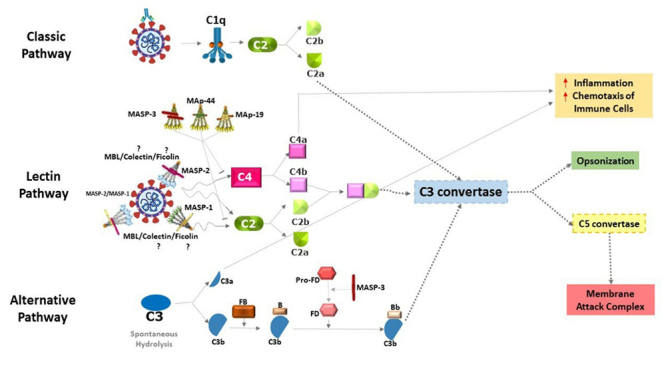
Figure 1 -. Complement pathways in SARS-CoV-2 infection. The activation of the classical pathway occurs through the C1 complex, after recognition of antibodies complexed to SARS-CoV-2. This leads to the cleavage of the C2 component into C2a and C2b. C2a joins the common pathway of the three complement pathways to form the C3 convertase. Activation of the lectin pathway by the virus via the MBL/MASP-1/MASP-2 complex has already been demonstrated, however the activation by ficolins or colectin is not shown (with a question mark). After binding of MBL/MASP complexes to the surface of pathogens, MASP-1 autoativates, transactivates MASP-2, and C2 and C4 components are cleaved (C2 and C4 by MASP-2 and C2 by MASP-1), generating the C3 convertase. The alternative pathway is initiated by the spontaneous hydrolysis of component C3, generating C3a and C3b. C3b binds to factor B and is cleaved by factor D, forming the C3 convertase of the alternative pathway. After this step, the three pathways converge into a single pathway. The C3 convertase enzyme cleaves component C3 into C3a and C3b. C3a and C4a are anaphylatoxins that contribute to an increase in inflammatory processes and to the chemotaxis of neutrophils and macrophages (red arrows), while C3b performs viral opsonization. The formation of C5 convertase occurs in different ways through the three pathways, but all generate C5a and C5b. C5a is an anaphylatoxin (as also C3a) that contributes to inflammatory processes, while C5b joins the last C6-C9 components of the cascade and forms the membrane attack complex. The MASP-3, MAp44, and probably MAp19 proteins inhibit the lectin pathway. MASP-3 also participates in the cleavage of pro-factor D into factor D, of the alternative pathway. The elements of the figure are not shown in their actual proportions.