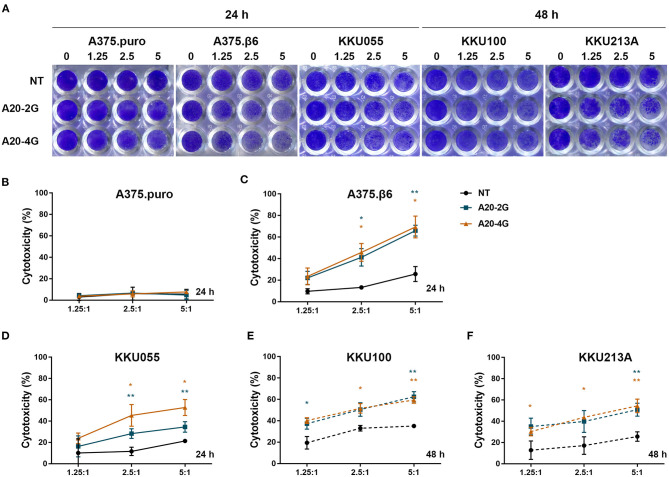
Figure 4.
Cytotoxic effects of A20-2G and A20-4G chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells on integrin αvβ6-negative A375.puro cells, integrin αvβ6-positive A375.β6 cells, and three integrin αvβ6-positive cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) cell lines, including KKU055, KKU100, and KKU213A. The effector CAR T cells were co-cultured with target cells at the indicated effector to target (E:T) ratios (1.25:1, 2.5:1, and 5:1) for 24 h (solid line) or 48 h (dashed line). (A) Cytotoxicity of target cells after co-culturing with effector cells quantified by crystal violet staining assay. Integrin αvβ6-negative A375.puro cell line served as negative control while integrin αvβ6-positive A375.β6 cells was served as positive control. (B) Cytotoxic effects of A20-2G and A20-4G CAR T cells on integrin αvβ6-negative A375.puro cells with non-transduced (NT) T cells used as a control for comparison. (C) Cytotoxic effects of A20-2G and A20-4G CAR T cells on integrin αvβ6-positive A375.β6 cells with NT T cells used as a control for comparison. Cytotoxic effects of A20-2G and A20-4G CAR T cells on integrin αvβ6-positive KKU055 (D), KKU100 (E), and KKU213A (F) cells as compared to the killing activity of NT T cells on the same target cells. Percentage of cytotoxicity relative to the total number of tumor cells alone (set at 0% cytotoxicity) from three independent experiments presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).