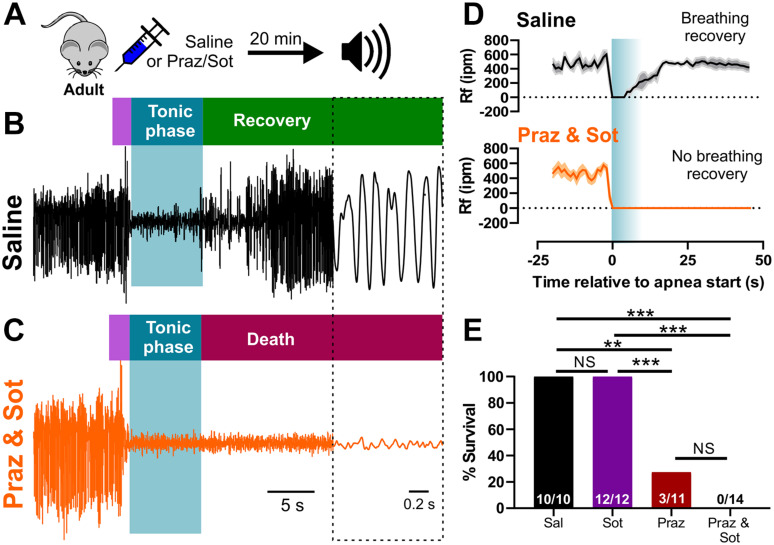
FIGURE 5.
Inhibition of adrenergic receptors leads to seizure-induced respiratory arrest and sudden death in adult D/+ mice. (A) Adult D/+ mice were injected (i.p.) with saline, prazosin (1 mg/kg) and/or sotalol (10 mg/kg) 15 min before stimulation of an audiogenic seizure. Example plethysmography recordings of breathing during audiogenic seizures in D/+ mice treated with saline [black; (B)] or prazosin and sotalol [orange; (C)] ∼15 min before acoustic stimulation. Breathing recovers in the saline-treated adult mouse. However, breathing never recovers in the combined prazosin and sotalol-treated adult mouse after the audiogenic seizure. (D) Average breathing rates (Rf ipm) for saline-treated (black; n = 4) and prazosin/sotalol-treated mice (orange; n = 5). (E) Bar chart of survival of adult D/+ mice treated with saline (black; n = 10), sotalol (purple; n = 12), prazosin (red; n = 11), and prazosin/sotalol (no color; n = 14). Prazosin alone significantly reduced survival rate compared to saline injection (***P < 0.001; n = 11), with a similarly strong effect observed in mice treated with both prazosin and sotalol (***P < 0.001; n = 14). Statistical comparisons made using one-sided Fisher’s exact tests.