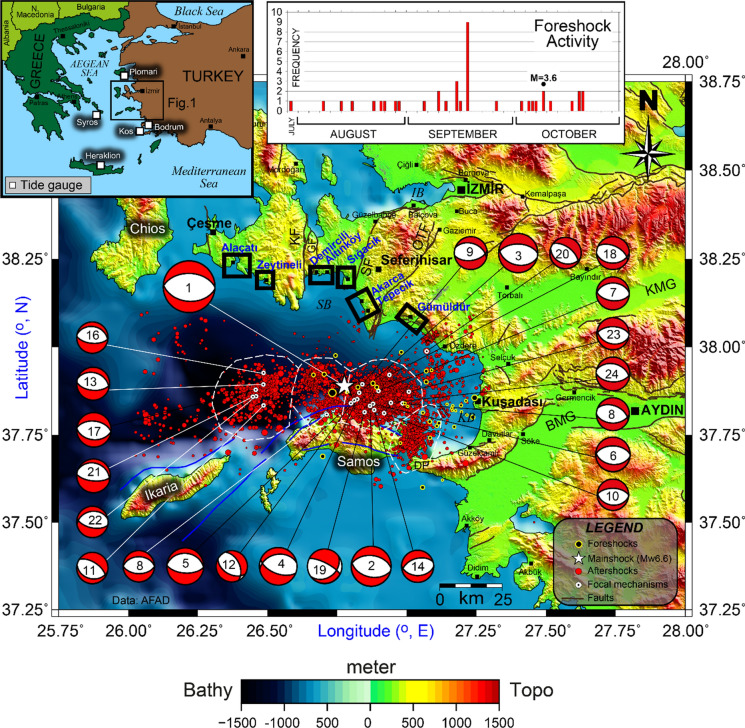
Fig. 1.
Seismotectonic map of Samos Island and its surroundings. The star shows the mainshock of 30 October 2020 Samos Island–İzmir earthquake (Mw 6.6). The beach balls present the focal mechanisms of the mainshock and the aftershocks given in Appendix 1, Table 1. The black and red circles indicate 3-month foreshocks and 2-month aftershocks, respectively, as of Ministry of Interior Disaster and Emergency Management of Presidency (AFAD 2020) data. Marine and terrestrial faults are compiled from Chatzipetros et al. (2013), Emre et al. (2013), Evelpidou et al. (2019), and Ring et al. (2017). The kinematic parameters of the focal mechanism solutions are given in Appendix 1, Table 1. (BMG Büyük Menderes Graben, DP Dilek Peninsula, GF Gülbahçe Fault, İB İzmir Bay, KF Karaburun Fault, KMG Küçük Menderes Graben, KB Kuşadası Bay, OTF Orhanlı-Tuzla Fault, SF Seferihisar Fault, SB Sığacık Bay). Black rectangles denote the post-tsunami survey localities. White rectangles represent tide gauges in the inset map. Bathymetric and topographic data are from EMODnet Digital Terrain Model (https://www.emodnet-bathymetry.eu)