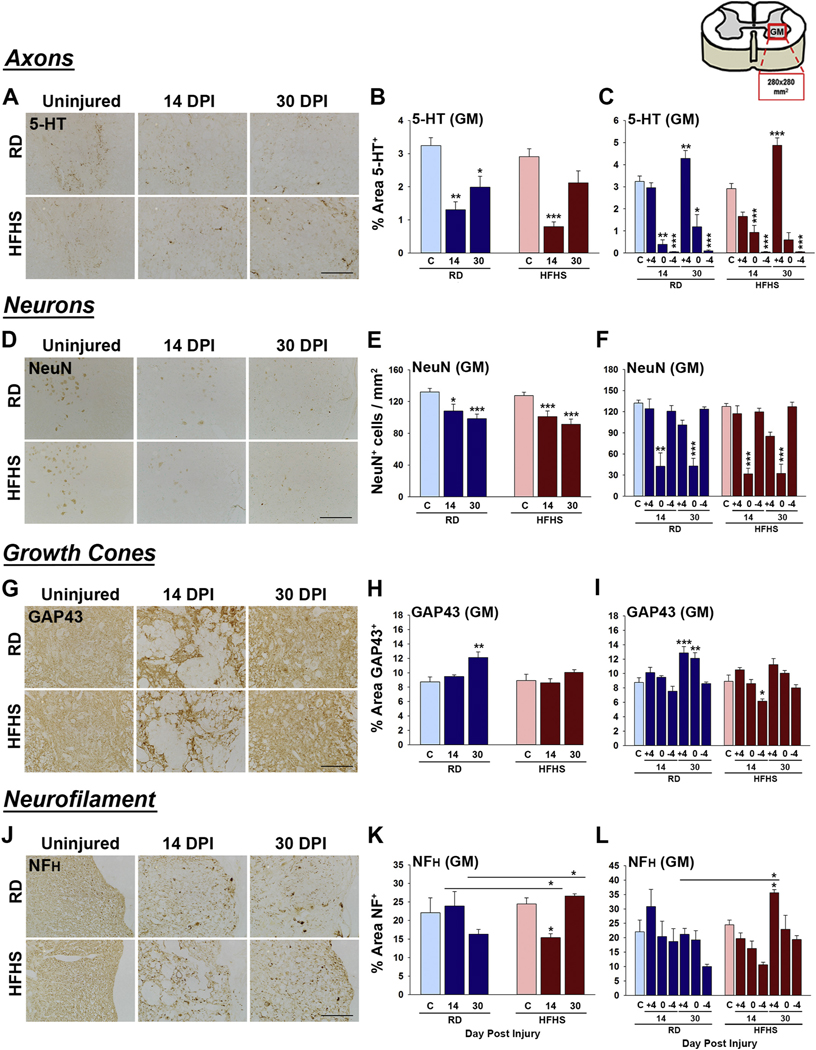
Fig. 4.
Signs of neural repair after SCI are impaired in mice consuming a Western diet. (A–C) Serotonergic 5-HT+ axons were reduced in spinal segments above the injury epicenter at 14 dpi in mice consuming HFHS compared to a RD. (D–F) The number of NeuN+ neurons in the ventral horn did not differ between groups. (G–I) GAP43-immunoreactive growth cones were reduced at 30 dpi the injury epicenter of mice consuming HFHS relative to a RD. (J–L) NFH-immunoreactivity was higher in mice consuming HFHS at 30 dpi (RD, uninjured n = 5, 14 dpi n = 4, 30 dpi n = 5 and HFHS, uninjured n = 5, 14 dpi n = 5, 30 dpi n = 5, female mice, *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, Two-way ANOVA, NK). Boxed area on cartoon of spinal cord shows area quantified. Representative images are shown in each case with scale bar = 100 μm (A, D and J), 200 μm (G). RD = regular diet, HFHS = high-fat high-sucrose.