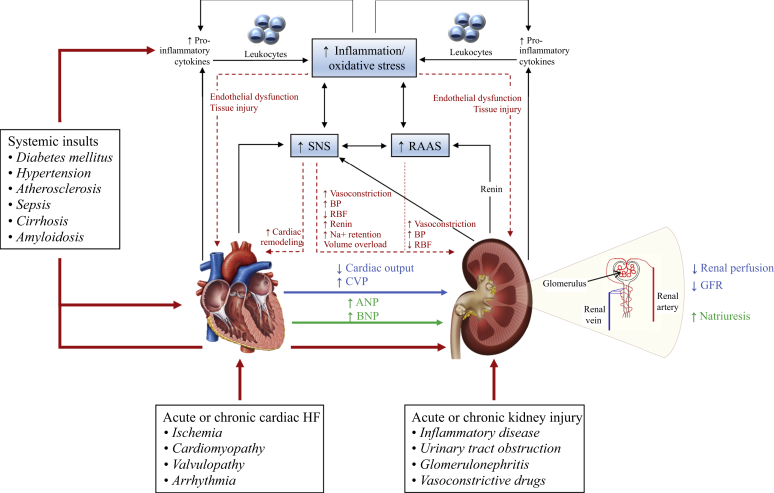
Figure 1.
A schematic diagram of the mechanisms underlying cardiorenal syndrome.1,24,26, 27, 28 Dysfunction in either the heart or kidneys, caused by systemic insults, triggers hemodynamic and nonhemodynamic changes, culminating in cardiorenal syndrome (CRS) and propagating a vicious cycle (double-headed black arrows). Black arrows indicate pathophysiological interactions in CRS; blue arrow, hemodynamic changes; dotted red arrows, consequences of nonhemodynamic changes; and green arrow, mechanism to correct renal function (decompensated). ANP, atrial natriuretic peptide; BNP, brain natriuretic peptide; BP, blood pressure; CVP, central venous pressure; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; HF, heart failure; Na+, sodium; RAAS, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; RBF, renal blood flow; SNS, sympathetic nervous system.