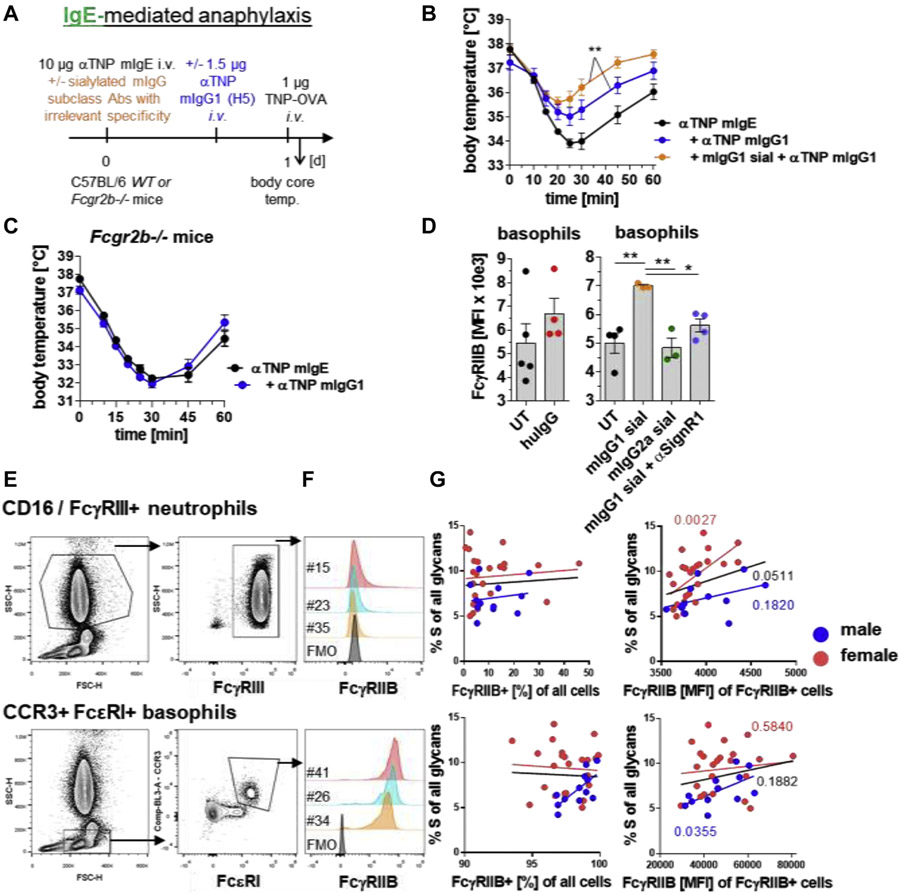
FIG 2.
Blood IgG sialylation levels are predictive for FcγRIIB expression levels and also attenuate IgG-FcγRIIB–controlled IgE-mediated anaphylaxis. A, Experimental design of the IgE-mediated anaphylaxis model used in the experiments shown in parts B and C. IgE-mediated anaphylaxis was induced i.v. with 10 μg of anti (α)-TNP murine (m) IgE (clone IgELa2) and i.v. injection of 1 μg of TNP-OVA 24 hours later. B and C, When indicated, i.v. injection of in vitro galactosylated plus sialylated (sial) mIgG1 (clone MOPC-21; 50 mg/kg) with irrelevant specificity and/or i.v. injection of 1.5 μg of αTNP mIgG1 (clone H5) into (Fig 2, B) WT or (Fig 2, C) Fcgr2b−/− mice. IgE-mediated anaphylaxis was induced as described in Fig 2, A. The severity of anaphylaxis in all experiments was measured by determining the changes in the body core/rectal temperature on the indicated time points after antigen challenge. n = 4-5 for all groups. D, When indicated, intraperitoneal injection of huIgG (IVIg; 1 g/kg) or i.v. injection of mIgG1 (clone MOPC-21; 50 mg/kg) or mIgG2 (clone C1.18.4; 50 mg/kg) with irrelevant specificities and/or αSIGN-R1 into WT mice to analyze FcαRIIB expression (MFI) on blood CD49b+/FcεRI+ basophils 24 hours later. n = 3-5 for all groups. Dots represent single mice. E, Human blood cell staining and gating strategies as indicated. F, Overlay histograms of FcγRIIB expression of the indicated cell populations and samples. G, Correlation of FcγRIIB expression on human neutrophils and basophils with serum IgG Fc sialylation levels. For correlating the expression levels of FcγRIIB with the IgG Fc sialylation levels, we focused on the percentages of FcγRIIB-expressing cells and the MFI of FcγRIIB on FcγRIIB-positive cells. FMO, Flourescence minus one; FSC-H, forward scatter-height; i.v., intravenous/intravenously; MFI, mean fluorescent intensity; SSC-H, side scatter-height; temp., temperature; WT, wild-type; UT, untreated.