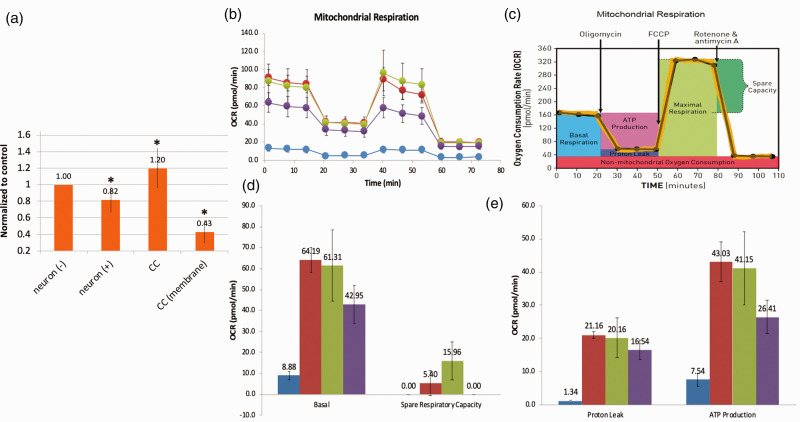
Figure 2.
Metabolic benefit of co-culture of MSC with oxidant-damaged neurons. Murine primary cortical neurons underwent in vitro oxidant injury with hydrogen peroxide followed by co-culture with MSC. (a) MTT assay. Neuronal cell viability declined after oxidant injury, improved after co-culture, but not if MSC were separated from neurons with a semi-porous membrane (CC membrane). (b–e) Seahorse XF Assay (pmol/min/60,000 cells). From left to right (see legend): MSC controls (blue); neuronal control (red); oxidant-damaged neurons in co-culture with MSC (green); neurons after hydrogen peroxide exposure (purple). (b) There is evidence of significant mitochondrial dysfunction in neurons after oxidant injury that recovers in co-culture with MSC when assessing mitochondrial respiration in neurons. If confidence intervals do not cross, differences are significant (see C for Figure key). (d) Basal mitochondrial respiration and spare respiratory capacity all worsened with oxidant injury and then improved with co-culture with MSC. (e) Proton leak and ATP production worsened in neurons after oxidant injury and recovered after co-culture. *Significant difference from control.