Figure 1.
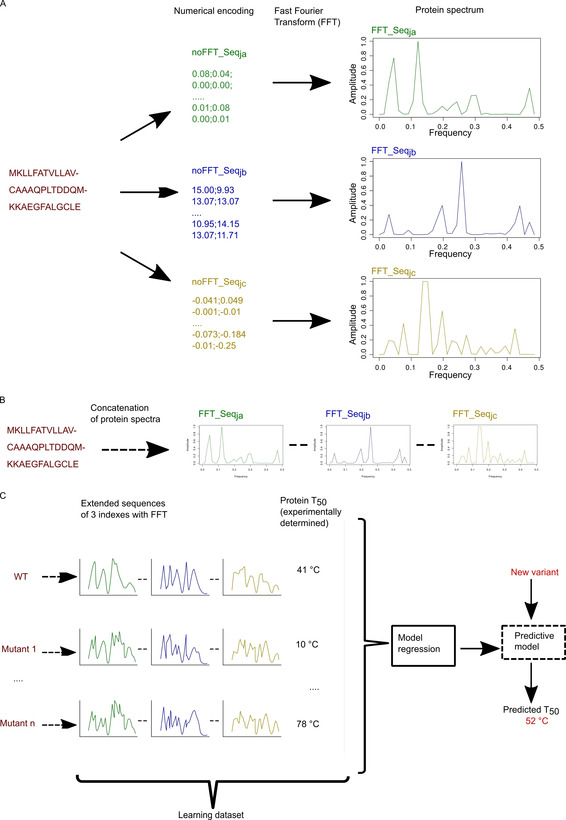
Workflow of the modelling process. A) A protein sequence is encoded in two steps: i) with numerical encoding based on an index of the AA index database, ii) FFT is applied to convert the encoded sequence into a protein spectrum. Each numerical encoding from an index will give a unique protein spectrum. Here three specific encodings give three specific protein spectra. Each protein spectrum is an elementary numerical sequence available for modelling with innov'SAR. B) Construction of a numerical extended sequence (Ext_SEQ) by concatenating the elementary numerical sequences. C) The different phases of innov'SAR: an encoding phase transforms the primary sequences of the initial dataset into protein spectra. The modelling phase uses the protein spectra and protein thermostability as a learning dataset in order to construct a regression model. Here, for the modelling of the epoxide hydrolase LEH, the construction of the model is based on a partial least‐squares regression method. Then the predictive phase uses the regression model and the protein spectra of new variants to predict their thermostability.
