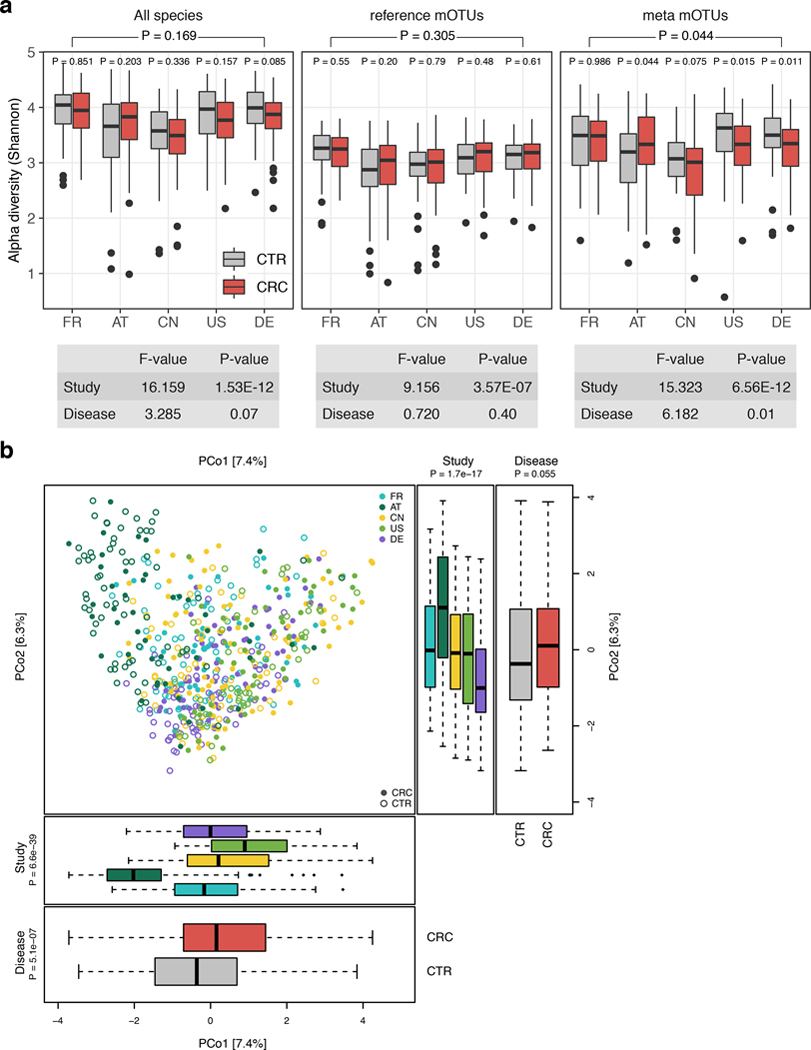
Extended Data Figure 2: Study shows a strong influence on alpha and beta diversity.
(a) Alpha diversity as measured by the Shannon index was computed for all gut microbial species (n=849), reference mOTUs (n=246), and meta mOTUs (n=603) separately. P-values were computed using two-sided Wilcoxon test, while the overall p-value (on top) was calculated using a two-sided blocked Wilcoxon test (n=575 independent observations, see Methods). Anova F statistics below the panel were computed using the R function aov. (b) Principal coordinate analysis of samples from all five included studies based on Bray-Curtis distance; study is color-coded and disease status (CRC vs control) indicated by filled/unfilled circles. The boxplots on the side and below show samples projected onto the first two principle coordinates broken down by study and disease status, respectively. P-values were computed using a two-sided Wilcoxon test for disease status and a Kruskal-Wallis test for study, (n=575 independent observations). For all boxplots, boxes denote the interquartile ranges (IQR) with the median as thick black line and whiskers extending up to the most extreme points within 1.5-fold IQR.