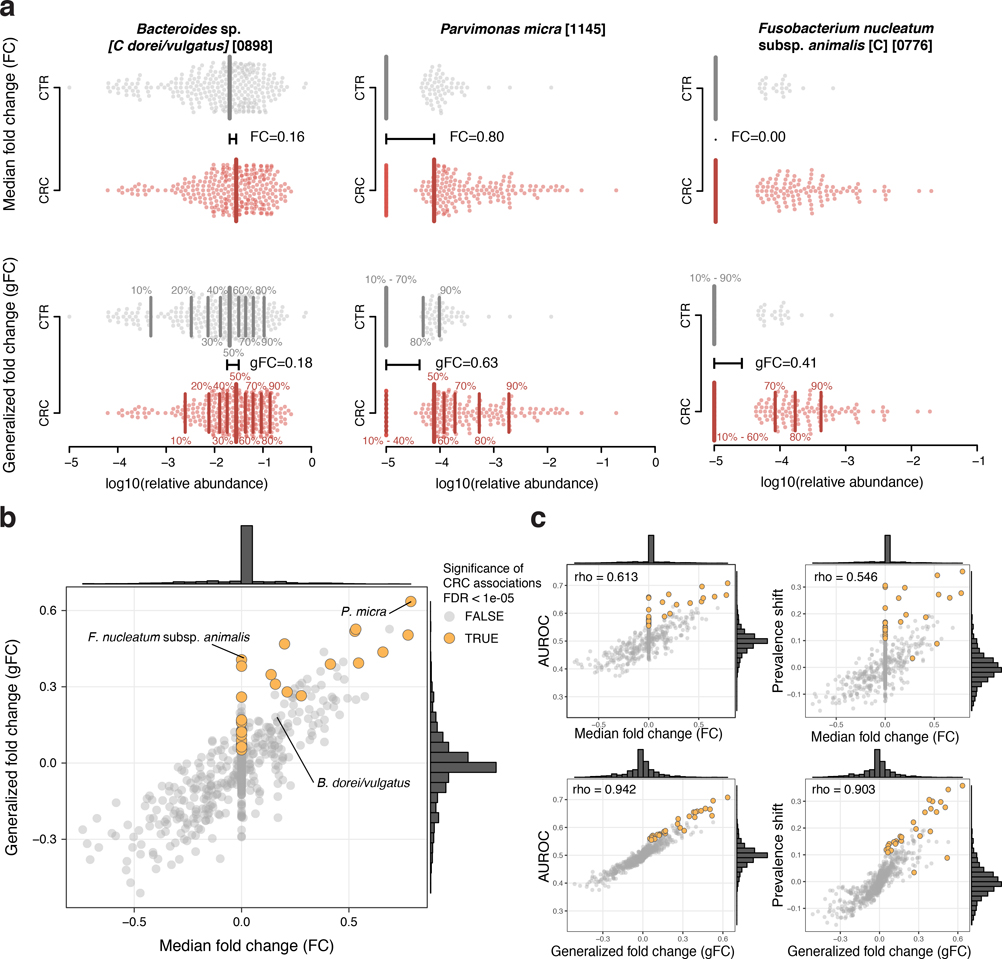
Extended Data Figure 3: The generalized fold change extends the established (median-based) fold change to provide higher resolution in sparse microbiome data.
(a) In the top row, the logarithmic relative abundances for Bacteroides dorei/vulgatus, Parvimonas micra, and Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. animalis -examples for a highly prevalent and two low-prevalence species- are shown as swarmplot for the control (CTR) and colorectal cancer (CRC) groups. The thick vertical lines indicate the medians in the different groups and the black horizontal line shows the difference between the two medians, which corresponds to the classical (median-based) fold change. Since Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. animalis is not detectable in more than 50% of the cancer cases, there is no difference between the CTR and CRC median and thus the fold change is 0. The lower row shows the same data, but instead of only the median (or 50th percentile), 9 quantiles ranging from 10% to 90% are shown by thinner vertical lines. The generalized fold change is indicated by the horizontal black line again, computed as mean of the differences between the corresponding quantiles in both groups. In the case of the sparse data (e.g. Fusobacterium), the differences in the 70%, 80% and 90% quantiles cause the generalized fold change to be higher than 0. (b) The median fold change is plotted against the newly developed generalized fold change (gFC) for all microbial species (core set of microbial CRC marker species highlighted in orange). Marginal histograms visualize the distribution for both FC and gFC. (c) Scatter plots showing the relationship between FC and gFC and area under the Receiver Operating Characteristics (AUROC) or shift in prevalence between CRC and CTR, with Spearman correlations added in the top-left corners; gFC provides higher resolution (wider distribution around 0) and better correlation with the nonparametric AUROC effect size measure as well as prevalence shift, which captures the difference in prevalence of a species in CRC metagenomes relative to control metagenomes.