FIGURE 5.
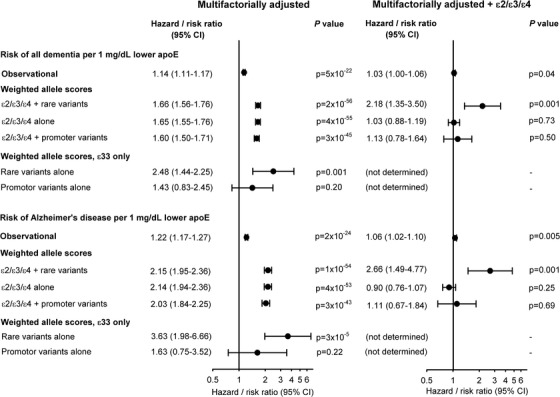
Risk for all dementia and Alzheimer's disease for a 1 mg/dL decrease in plasma apolipoprotein E (apoE) levels. Cox regression models were adjusted for age (time scale), sex, body mass index, smoking, hypertension, diabetes, lipid‐lowering therapy, alcohol consumption, physical inactivity, postmenopausal status, hormonal replacement therapy, and education (left column), and further for APOE ε2/ε3/ε4 genotype (right column). For the observational estimates, follow‐up began at study entry and only if plasma apoE measurements were available, thus including 103,744 individuals in these analyses. The first weighted allele score, ε2/ε3/ε4 + rare variants, is the score described in the Methods section (n = 105,597). For the second score, ε2/ε3/ε4 alone, the score was obtained similarly, but in a model only including the ε4 and the ε2 alleles, and not the nine rare variants (n = 105,597). The third score, ε2/ε3/ε4 + promoter variants, was obtained like the main genetic score, but included weights from ε4, ε2, and three common promoter variants (rs449647, rs769446, and rs405509) (n = 74,940). The estimates for rare variants alone and for promotor variants alone were for the same genetic scores for ε33 individuals only (n = 58,737 and 41,789). CI, 95% confidence interval
