FIGURE 1.
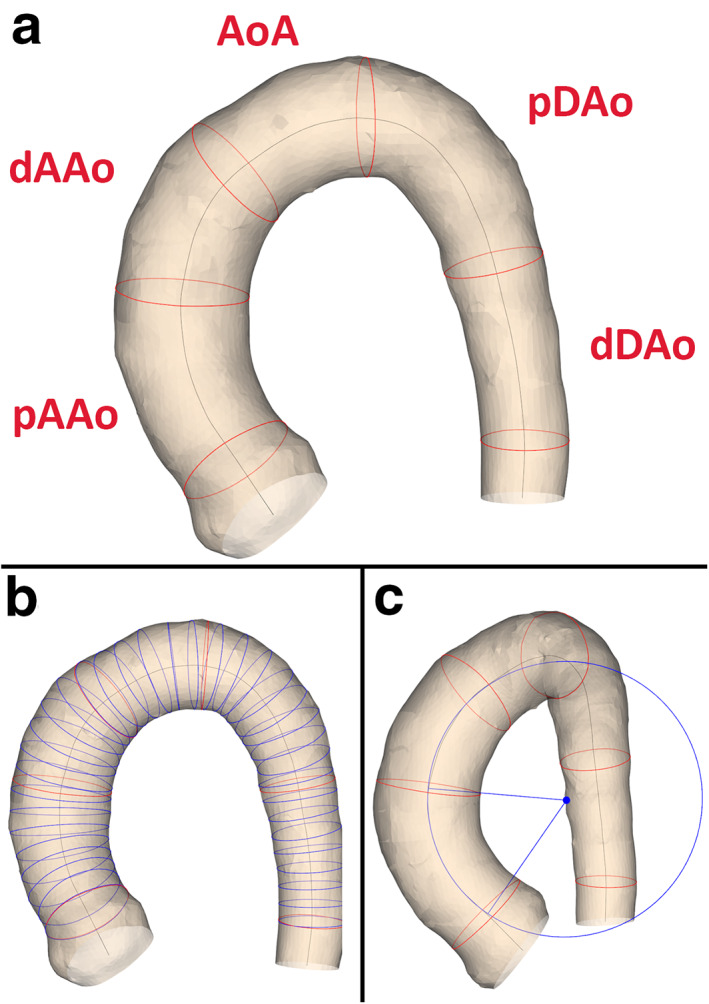
The aortic lumen segmentation with (a) the anatomical segments, (b) the lumen cross‐section to derive maximal diameter, (c) and a circle fitted to the proximal ascending aorta. Example of an aorta lumen segmentation of a healthy volunteer. (a) The anatomical segments. (b) The cross‐sections to derive the lumen diameter. To improve visibility, the cross‐sections are displayed every 5 mm instead of every mm that was used during the analysis. (c) A circle fitted to the proximal ascending aorta. pAAo = proximal ascending aorta (from the sinotubular junction to the mid‐ascending aorta), dAAo = distal ascending aorta (from the mid‐ascending aorta to the brachiocephalic artery), AoA = aortic arch (from the brachiocephalic artery up and including the left subclavian artery), pDAo = proximal descending aorta (from the left subclavian artery to the mid‐descending thoracic aorta) and dDAo = distal descending (from the mid‐descending thoracic aorta to the descending aorta at the level of the aortic valve).
