FIG. 2.
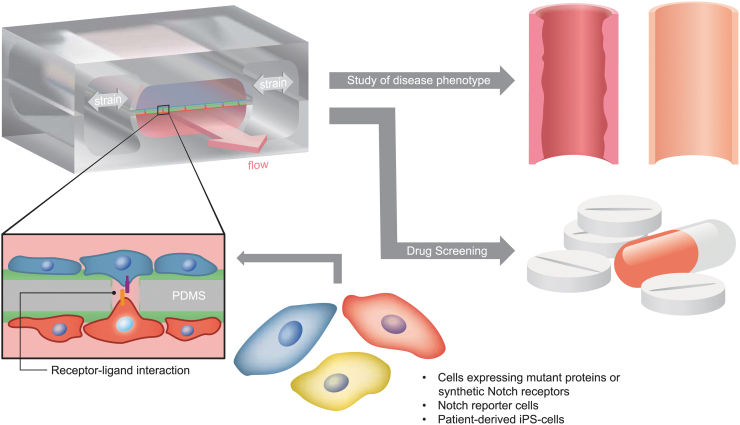
Microphysiological systems mimicking specific features of the cellular environment can enable the study of diseases caused by Notch mutations. For example, patient-derived or other human cells can be inserted in microfluidic devices mimicking the layer separation between endothelial cells and VSMCs, which is evident in blood vessels not only in terms of location but also stimuli (shear stress and cyclic stretch for endothelial cells and only cyclic stretch for VSMCs). These devices provide platforms where Notch interactions can be efficiently quantified, thereby enabling the controlled investigation of disease phenotypes and drug screening with donors' cells (the scheme of the microfluidic device is adapted from Ref. van Engeland et al.61). VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cell.