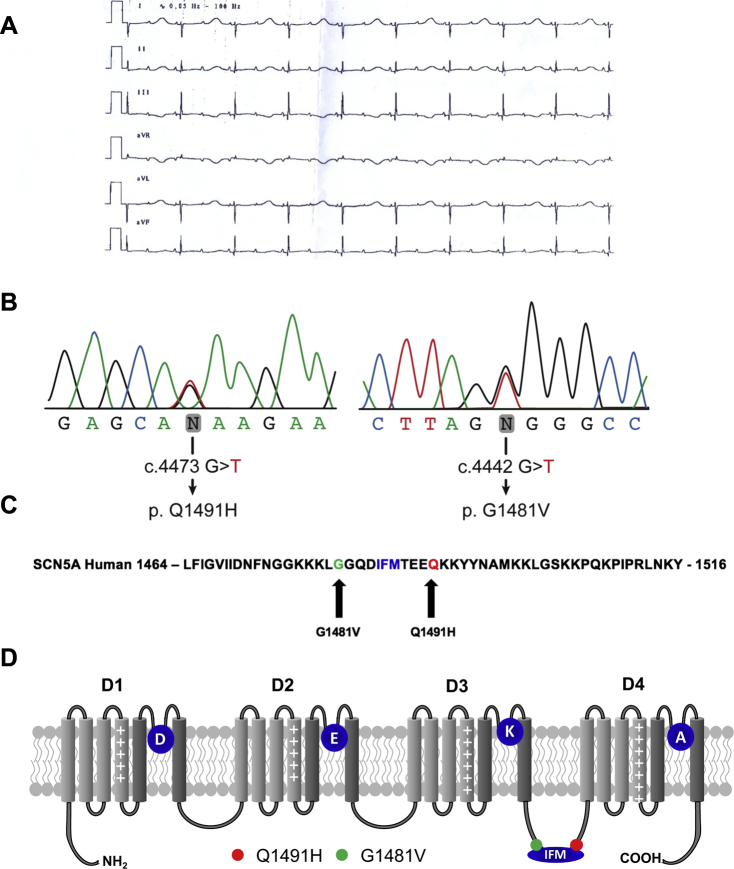
Figure 1.
(A) A standard electrocardiogram was recorded soon after birth. Paper speed was 25 mm/s; 10 mm/1 mV. The QT interval was 720 ms; the QRS was 60 ms; and 2:1 atrioventricular block developed due to an extremely prolonged QT interval. (B) Sequence analysis of the G1481V and Q1491H mutations. (C) The Q1491H mutation resulted from a G-to-T substitution at position 4473, leading to a glutamine (Q)-to-histidine (H) substitution at residue 1491. The G1481V mutation resulted from a G-to -T substitution at position 4442, leading to a glycine (G)-to-valine (V) substitution at residue 1481. (D) Schematic representation of the 4 domains of the α-subunit of the Nav1.5 channel showing the locations of the Q1491 and G1481V mutations. DEKA represents the selectivity filter of the channel. The Q1491H mutation caused a glutamine-to-histidine substitution 4 amino acids downstream from the isoleucine, phenylalanine, and methionine motif. The G1481V mutation caused a glycine-to-valine substitution 4 amino acids upstream from the isoleucine, phenylalanine, and methionine motif.