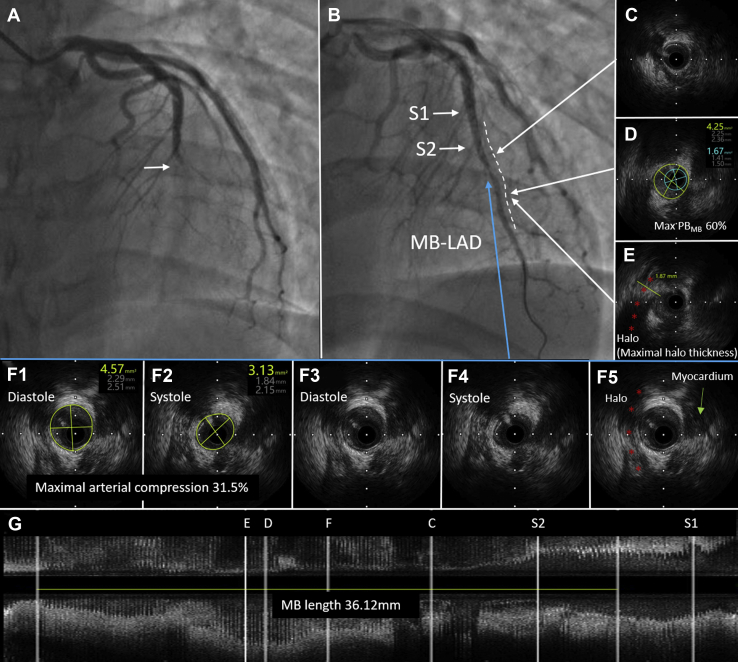
Figure 1.
Myocardial bridging (MB) and culprit lesions in acute coronary syndrome. (A) Angiographic appearance of culprit lesions in the mid-left anterior descending (LAD) artery (white arrowhead). (B) Angiographic appearance of opened coronary artery and MB in mid-LAD (white dashed line). (C) Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) image of proximal MB. (D) Maximum plaque burden in the MB segment (Max PBMB) was 60%. (E) Site with maximal halo thickness. (F) Site with maximal arterial compression. (G) Longitudinal IVUS view. MB was identified by IVUS as an echolucent-band “halo” (red asterisk; E, F). S1, septal 1; S2, septal 2.