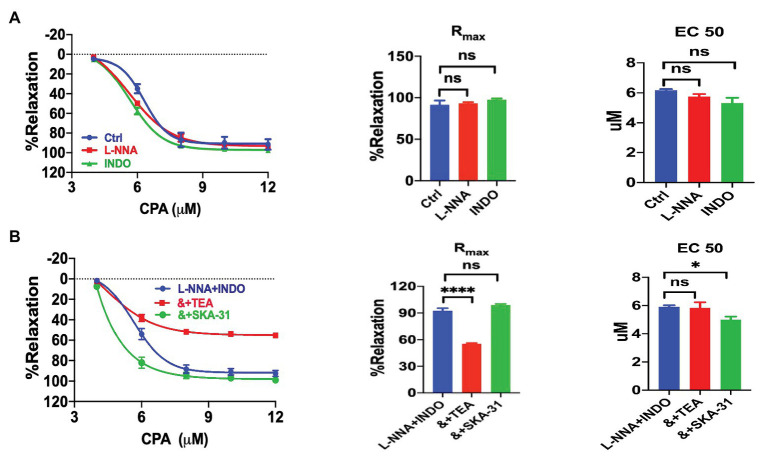
Figure 3.
Cyclopiazonic acid induction of mesenteric arterial relaxation through endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization. (A) Summary data showing the CRC, Rmax, and EC50 of CPA-induced vasorelaxation in mesenteric arteries in the absence (control, n = 6) or the presence of either 100 μM Nω-nitro-L-arginine (L-NNA; n = 6) or 10 μM indomethacin (INDO; n = 6). (B) Summary data showing the CRC, Rmax, and EC50 of CPA-induced vasorelaxation in the presence of L-NNA + INDO (n = 6), L-NNA + INDO (&) + 0.3 μM SKA-31 (n = 6), or L-NNA + INDO (&) + 10 mM tetraethylammonium chloride (TEA; n = 6). Data were expressed as percentage of NE (5 μM)-induced vasoconstriction and shown as means ± SEM. *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001, and ns, no significance.