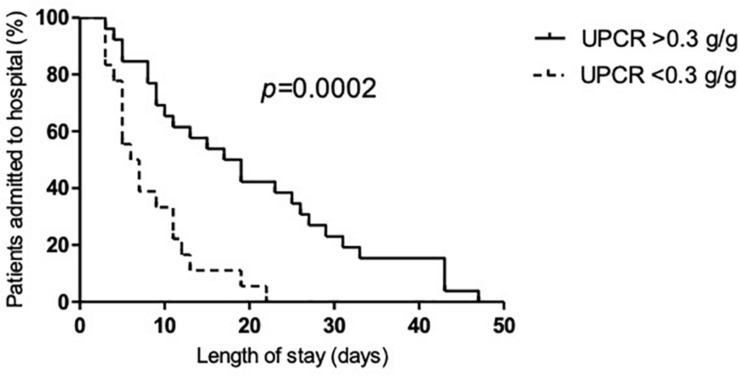
FIGURE 1.
Significant proteinuria is associated with an increased risk to develop severe disease and longer hospitalization in patients with COVID-19 disease. Patients with higher proteinuria presented an increased risk to develop severe disease and to require admission to the intensive care unit. Kaplan-Meier analysis of the effect of proteinuria >0.3 g/g on length of stay in patients hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 infection showed that patients with proteinuria greater than 0.3 g/g presented a longer hospitalization (log-rank p = 0.0002).