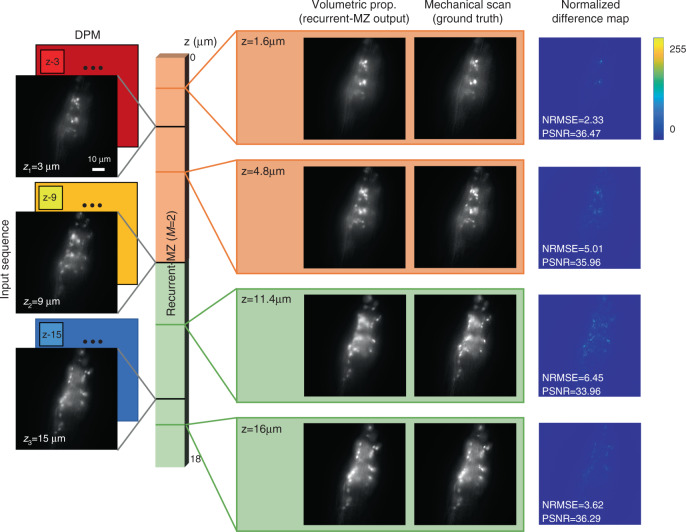
Fig. 2. Volumetric imaging of C. elegans from sparse wide-field scans using Recurrent-MZ.
The DPMs in the input sequence are used to define an arbitrary axial position (z) within the sample volume. In this implementation, Recurrent-MZ takes in 2 input scans (M = 2) to infer the image of an output plane, as indicated by the color of each output box. See Video S1 to compare the reconstructed sample volume inferred by Recurrent-MZ against the ground truth, |Z| = 91 images captured with an axial step size of 0.2 μm