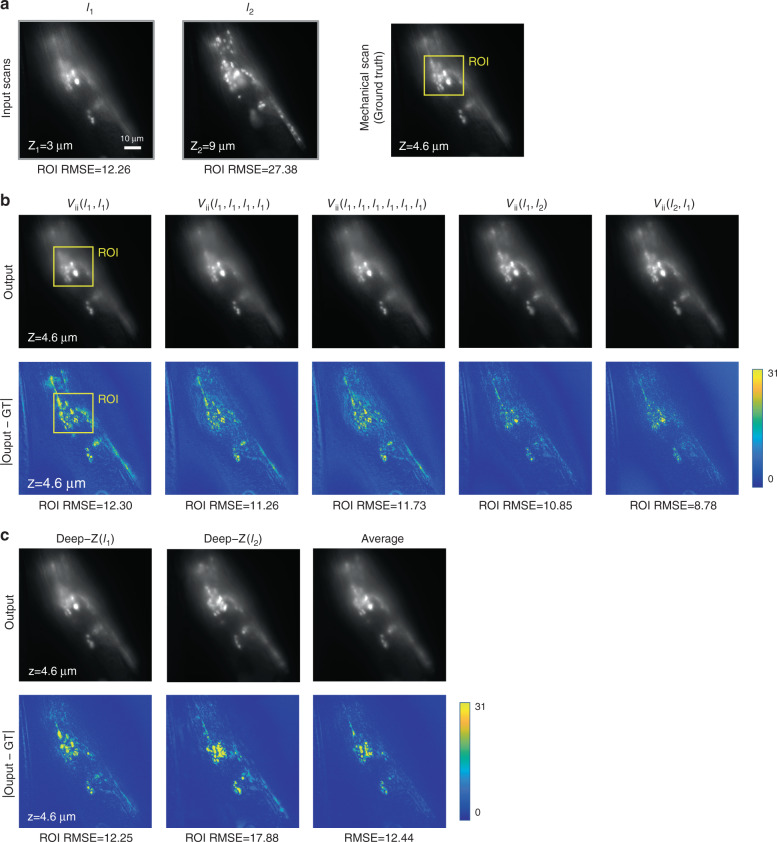
Fig. 7. Repetition invariance of Recurrent-MZ.
Recurrent-MZ was trained with inputs (M = 2) sorted by their relative distances (dz) to the output plane, but tested on a new sample by repeatedly feeding the input image (I1) to test its repetition invariance. a The input images and the ground truth image obtained by mechanical scanning (with an axial spacing of 0.2 μm), b the Recurrent-MZ outputs and the corresponding difference maps of repeated I1, i.e., Vii(I1, I1), Vii(I1, I1, I1, I1) and Vii(I1, I1, I1, I1, I1, I1) as well as Vii(I1, I2) and Vii(I2, I1), c the outputs and corresponding difference maps of Deep-Z with a single input image (I1 or I2), and the pixel-wise average of Deep-Z(I1) and Deep-Z(I2). All RMSE values are calculated based on the region of interest (ROI) marked by the yellow box. The range of grayscale images is 255 while that of the standard variance images is 31