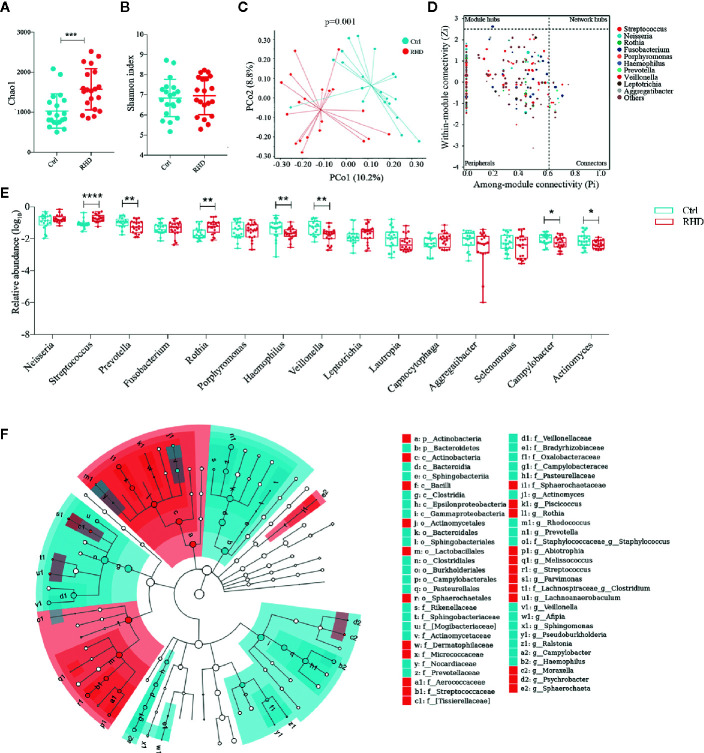
Figure 3.
Alterations of salivary microbiota in patients with rheumatic heart disease. Microbiota of saliva from patients with rheumatic heart disease (RHD) and control subjects (Ctrl) were analyzed using 16S rRNA gene sequencing. (A) Richness of salivary microbiota assessed by Chao1. (B) α-diversity of salivary microbiota assessed by Shannon index. (C) β-diversity analyzed by principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) based on Bray–Curtis distance of salivary microbiota at genus level. (D) Determination of module-based topological roles (peripherals, connectors, module hubs, or network hubs) of salivary microbiota in RHD patients using ZP-plot at genus level. The size of dots represents abundance of each genus. (E) Relative abundances of the fifteen most abundant genera in salivary microbiota. (F) Taxonomic cladogram of salivary microbiota based on LEfSe. Red color indicates increase and blue indicates decrease of taxa in RHD compared to Ctrl. LDA = 3. Mann–Whitney test was used. n = 20: 20. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.