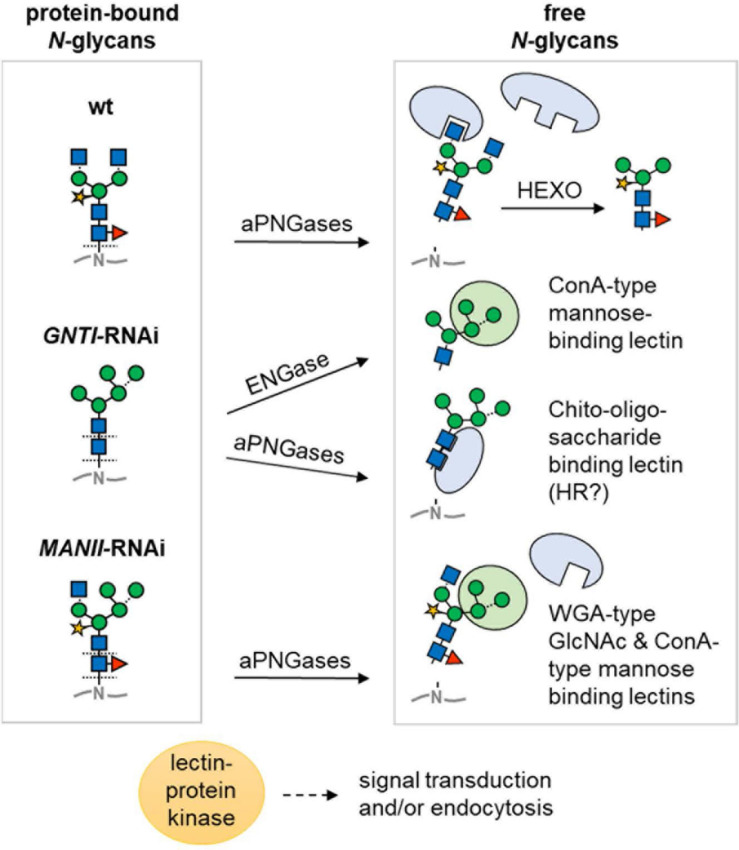
FIGURE 10.
Model of differential N-glycan interpretation in the RNAi lines. Protein-bound N-glycans of wild-type (wt), GNTI-RNAi, or MANII-RNAi plants (left) may be either directly bound or liberated depending on capability for enzymatic release. Decoding is suspected to occur by proteins with lectin domains (for sugar symbols, see Figure 3A). Arrows indicate cleavage by peptide:N-glycosidase (PNGase A isoforms in different acidic compartments that may release core fucosylated N-glycans) or in the cytosol by endo-β-N-acetyl-glucosaminidase (ENGase). In GNTI-RNAi plants, the chito-oligosaccharide N-glycan core may be decoded upon release from the glycoprotein backbone, potentially resulting in HR (hypersensitive response). Abbreviations: ConA, concanavalin A; HEXO, hexosaminidases (apoplast/vacuole); WGA, wheat-germ agglutinin.