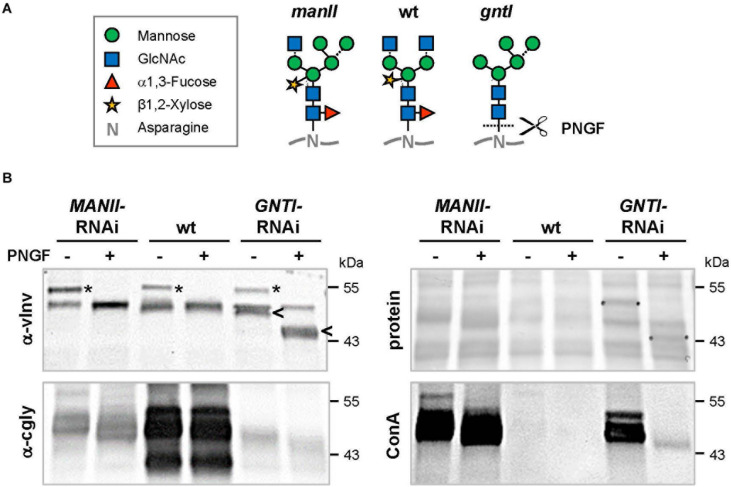
FIGURE 3.
Peptide:N-glycosidase F (PNGase F) treatment verifies the presence of core fucoses on MANII-RNAi glycans. (A) N-glycan structures (www.proglycan.com) that may be produced in wild-type (wt), manII, and gntI mutant plants (known as hgl1 and cgl1 in Arabidopsis, respectively) with indicated potential release by PNGase F. This endoglycosidase can cleave asparagine-bound N-glycans when coreα1,3-fucose is missing. In the cell wall or vacuole, terminal sugar residues can be liberated by hexosaminidases (GlcNAc) and α-mannosidases (dotted lines). (B) Immunoblots of untreated (-) and PNGase F-treated (+) fruit extracts from MANII-RNAi (#14), Micro-Tom wild-type (wt), and GNTI-RNAi (#20) plants were developed with α-vINV, α-cgly (α-PHA-L), or the lectin ConA (detecting mannose-terminating N-glycans). The Ponceau S-stained blot (protein) is shown as the loading reference. In GNTI-RNAi, PNGase-F treatment results in a shift of vacuolar invertase (vINV, arrowheads) and loss of ConA binding. This is not the case for MANII-RNAi or wt samples, confirming the presence of core fucoses on most glycoproteins. Note that the upper band detected by α-vINV (stars) shifts in all PNGase F-treated extracts (protein with high mannose precursor), indicating completeness of the enzyme treatment. Apparent molecular masses are indicated in kDa (PageRuler Prestained Protein Ladder, Fermentas).