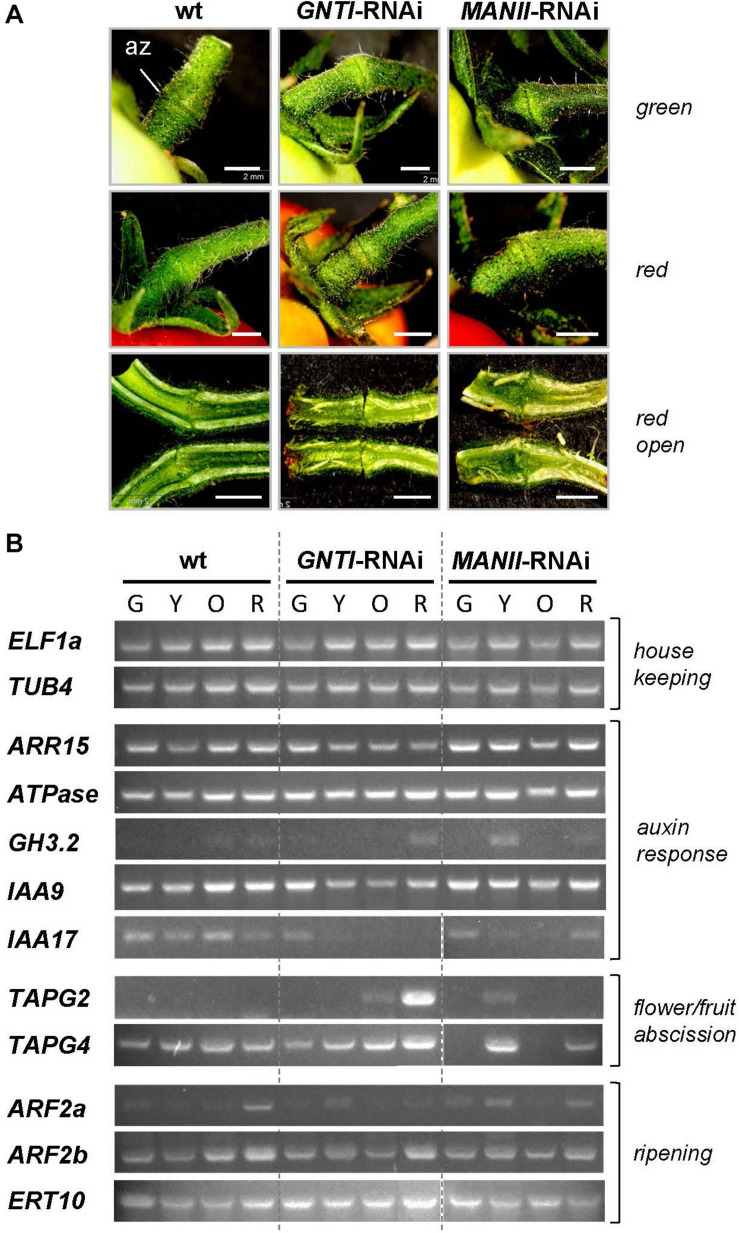
FIGURE 8.
Marker gene expression in wild-type, GNTI-RNAi, and MANII-RNAi fruit pedicels. (A) Close-up view of pedicels attached to green (top) or red (ripe) fruits of Micro-Tom wild-type (wt), GNTI-RNAi (#20), and MANII-RNAi (#18). Parts ca. 3 mm to both sides of the abscission zone (az) were used for RNA isolation. Longitudinally cut open pedicels of red fruits are shown below. Fruits were attached to the left. Bars = 2 mm. (B) Semiquantitative RT-PCR of abscission zones of GNTI-RNAi (#20) and MANII-RNAi (mix of #11 and #18) with green (G), yellow (Y), orange (O), or red (R) fruits was performed with two housekeeping genes as reference: ELF1a, translation elongation factor; TUB4, tubulin 4 (top). Marker genes were chosen based on known responses to auxin/ethylene and expression during certain developmental stages (abscission, fruit ripening). ARR15, Arabidopsis response regulator type A, auxin-responsive-negatively regulating cytokinin; ATPase (H+), auxin/sugar-responsive; GH3.2, IAA-amido synthetase, auxin- and ethylene-responsive; IAA9/17, AUX/IAA transcription factors: IAA9, auxin-responsive, ethylene-repressed; important for leaf morphology/fruit set; IAA17, auxin-responsive, ethylene-repressed; TAPG2/4, tomato abscission-related polygalacturonases; ARF2a/b, auxin response factors important for tomato fruit ripening (auxin versus ethylene); ERT10, tomato ripening-related marker.