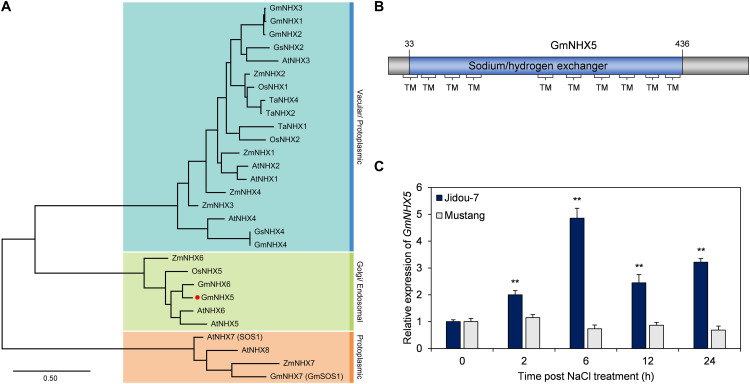
FIGURE 1.
Characterization and expression of GmNHX5. (A) Phylogenetic analysis of GmNHX5 and its homologs from other plants. Protein sequences of NHXs from several plants were used for phylogenetic analysis using the maximum likelihood method and JTT matrix-based model. Species abbreviated as: Ta, Triticum aestivum; Os, Oryza sativa; Zm, Zea mays; Gm, Glycine max; Gs, Glycine soja; At, Arabidopsis thaliana. Red dot emphasizes GmNHX5 used in this study. Colored sections indicate potential subcellular localization of corresponding proteins retrieved from UniProtKB. The scale bar indicates the number of amino acid substitutions per site. (B) Structural domains of GmNHX5. The colored section indicates Na+/H+ exchanger functional domain, Braces indicate transmembrane (TM) domains. (C) Relative expression of GmNHX5 under salt stress. RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression of GmNHX5 in soybean Jidou-7 and Mustang at 200 mM NaCl for the corresponding time. Actin was used as a reference gene. Each value represents the mean ± SE of three biological replicates relative to 0 h. Asterisks above the bars indicate significant differences from the values measured in Mustang (P < 0.05 by Student’s t-test).