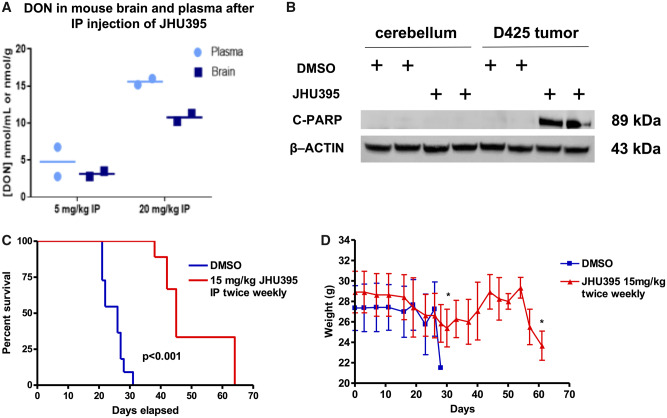
FIGURE 7.
Isopropyl 6-diazo-5-oxo-2-(((phenyl (pivaloyloxy) methoxy) - carbonyl) amino) hexanoate (JHU395) administration leads to micromolar levels of 6-diazo-5-oxo-l-norleucine (DON) in brain as measured by mass spectrometry with resulting increase in survival of mice bearing medulloblastoma orthotopic xenografts. (A) Parenteral administration of JHU395 dosing at 5 or 20 mg/kg in Nu/Nu mice led to the accumulation of micromolar concentrations of DON in brain as measured by mass spectrometry. IP dosing resulted in an average 0.66 brain-to-plasma ratio. The brain had an average concentration of 11.3 nmol/ml of DON after 20 mg/kg JHU395 intraperitoneal administration. (B) Single treatment of JHU395 after 72 hours showed significant effect in inducing apoptotic cells death specifically on D425MED but not on normal cerebellum. (C) Twice weekly 15 mg/kg dosing of JHU395 significantly extended the survival of athymic nude mice with D425MED tumors. Red line, JHU-395; blue line, vehicle. p < 0.001 comparing treated vs vehicle control as determined by Log-rank test n = 10 animals in the control group and n = 9 animals in the treatment group). (D) Representative graph shows the mouse weights were stable during the treatment course. At week 3 of the study, mean mouse weight reduced around 10% but then subsequently recovered back to baseline. Both control and treatment mice lost weight in the few days immediately before death due to progression of tumor.