Fig. 3. Characterization and Performance of a PAP Patient-Derived GMAb Polyclonal Reference Standard (PCRS).
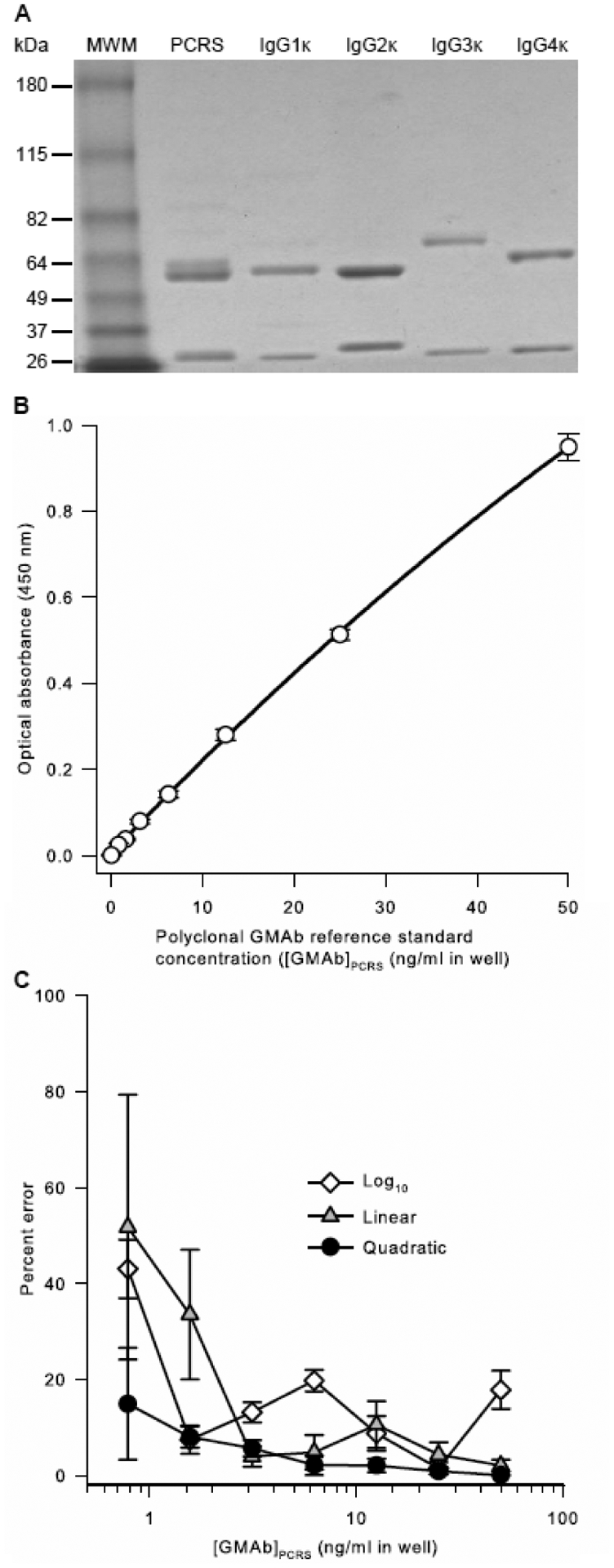
A. Purity and composition of the PCRS. PCRS, prepared as described in the methods, commercially available IgG heavy chain isotype standards (IgGκ 1, 2, 3, or 4), or molecular weight markers (MWM) were subjected to polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under reducing conditions, Coomassie blue staining, and photography as described in the methods.
B. Optical Absorbance of the PCRS as a Function of Concentration. The PCRS was serially diluted and evaluated as the standard in the GMAb ELISA as described in the methods. Optical absorbance increased smoothly in proportion with PCRS concentration. Regression analysis using a quadratic equation yielded a correlation coefficient (R2) of 0.9998. Each point represents the mean (+SD) of 5 separate measurements.
C. Effect of Regression Method Used on Percent Error of the PCRS Curve Rit. Results from 5 independent, simultaneously conducted experiments determining the optical absorbance of serial dilutions of the PCRS were subjected individually to linear, quadratic, or logarithmic regression analysis and the mean (±SD) percent deviation at each concentration was determined. The percent error of GMAb concentration was determined as the measured value minus the expected value divided by the expected value and multiplied by 100. The mean (±SD) correlation coefficients for regression analysis of 5 separate experiments (not shown) were 0.9999 ± 0.0001 (quadratic), 0.9969 ± 0.0029 (log10), and 0.9819 ± 0.0043 (linear).
