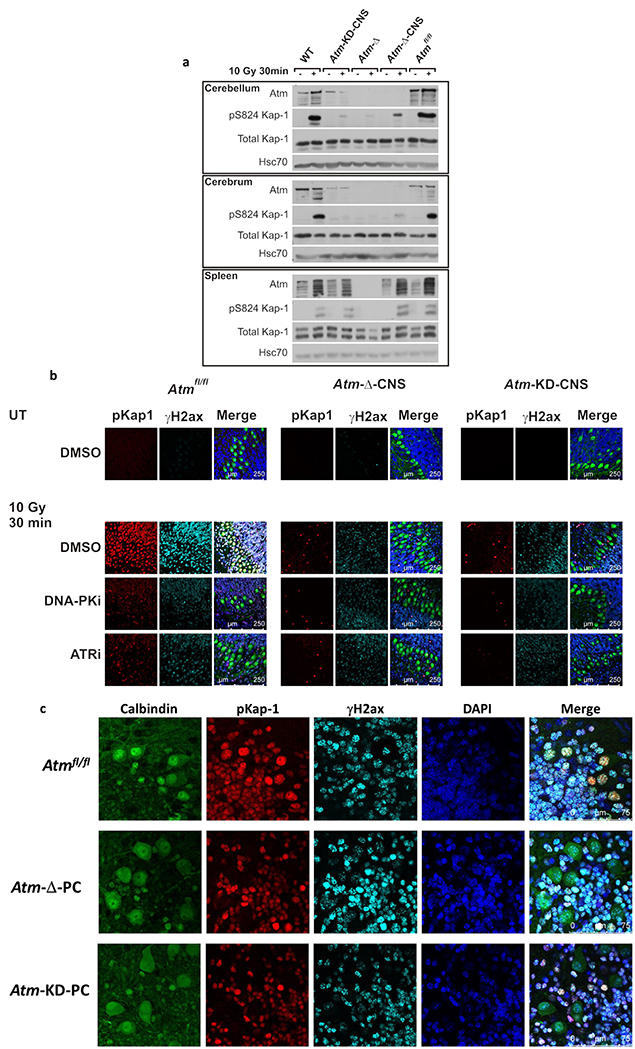
Fig. 2. AtmKD expression in the CNS and functional consequences.
a. Western blotting analysis of cerebellum, cerebrum and spleen with different genotypes after whole-body irradiation with 10 Gy of IR. Phosphorylation of the Atm substrate, Kap-1, 30 min after irradiation was used as a readout of Atm activity in response to DNA damage. b. Immunostaining of phosphorylated Kap-1 in organotypic cerebellar cultures established from P12 mice. Cultures were pretreated with DMSO or 5 μM NU7441 – a DNA-PK inhibitor (DNA-PKi), or 0.5 μM AZ20 – an ATR inhibitor (ATRi), and irradiated with 10 Gy of IR. The merged images include Calbindin D28k staining (green), which labels PCs and DAPI staining (blue), which labels cell nuclei. c. Similar analysis as in (b) in cerebellar organotypic cultures derived from WT, Atm-Δ-PC and Atm-KD-PC mice. Note the lack of Kap-1 phosphorylation in PCs only, in both genotypes. PCs are marked by Calbindin D28k staining (green).