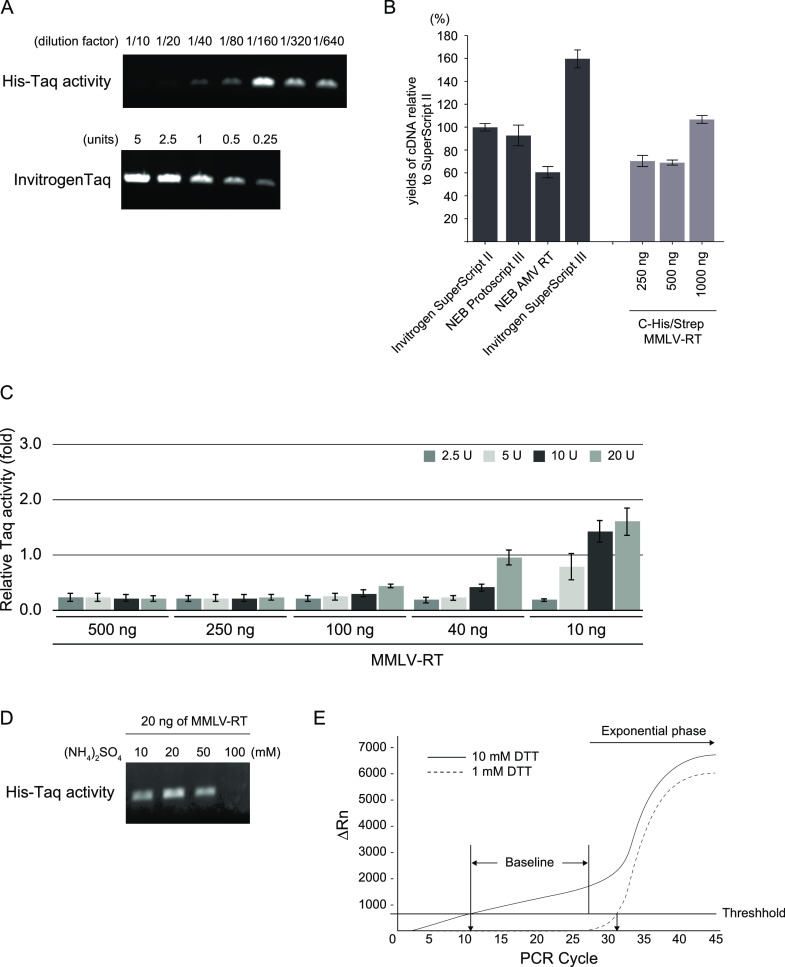
Figure 3.
(A) Activity assays of His-Taq Pol and N-Taq Pol by PCR. Purified His-Taq Pol was serially diluted by the storage buffer (see the Materials and Methods section) with the indicated dilution factors and subjected to the PCRs. N-Taq Pol is the same as in Figure 2C, and the standard titration curve made by N-Taq Pol is shown in the Supporting Information. (B) Activity assays of C-His/Strep MMLV-RT and other commercially available reverse transcriptases. The first-strand cDNA was synthesized from SARS-CoV-2 N gene RNAs, and the 2019-nCoV_N3 qPCR assay was conducted. The yields of cDNA synthesis are shown in the ratio of each reverse transcriptase to SuperScript II. Error bars represent standard errors. (C) MMLV-RT inhibitory effect on Taq Pol activity in the PCR. The indicated amounts of purified C-His/Strep MMLV-RT were added to the PCR premixture containing different units of Taq Pol. Error bars represent standard errors. (D) Ammonium sulfate eases the inhibitory effect of MMLV-RT on Taq Pol’s activity in PCR. The different amounts of ammonium sulfate were added to the PCR mixture without C-His/Strep MMLV-RT, and subsequently, 20 ng of C-His/Strep MMLV-RT was added to the reaction. (E) Effect of the DTT concentration on the baseline of the TaqMan-based detection system. The one-step qRT-PCR was performed with 1000 copies of the synthetic RNAs as a template. ΔRn; Rn is the fluorescence of the reporter dye divided by the fluorescence of a passive reference dye, and ΔRn is Rn minus the baseline.