Figure 3.
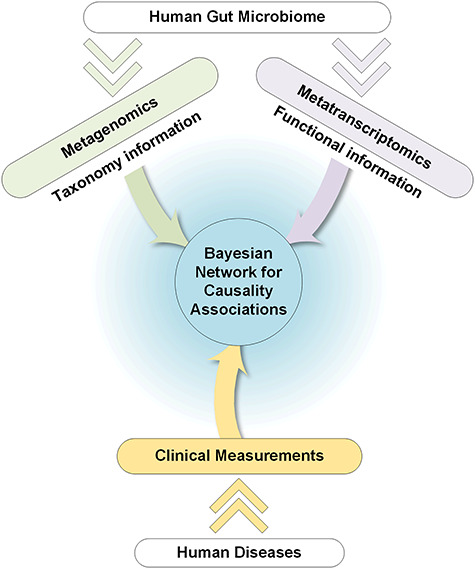
The exploration of host–microbiome relationships in the context of human health and disease. The gut microbiome plays an influential role in human diseases, including cancer, chronic diseases and inflammatory diseases. Integrated metagenomic and metatranscriptomic data of the microbial community with clinical measurements of the specific disease can unravel causal relationships between the microbiome and diseases, using the Bayesian network approaches for an example.
