Fig. 3.
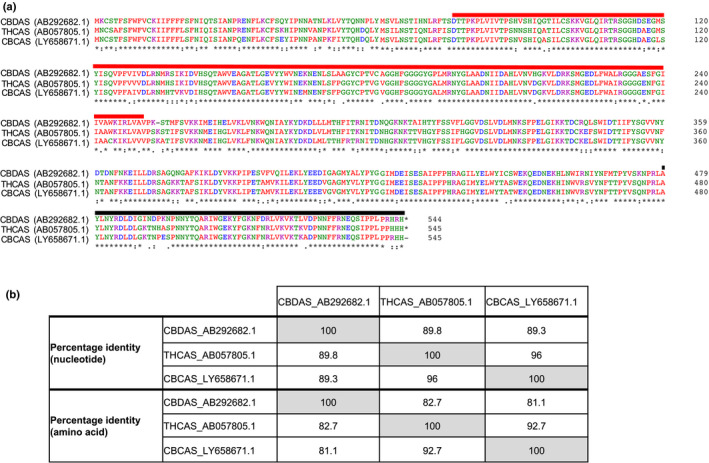
Sequence similarity between the Cannabis sativa cannabinoid synthase genes tetrahydrocannabinolic acid synthase (THCAS; GenBank acc. no. AB057805.1), cannabidiolic acid synthase (CBDAS: GenBank acc. no. AB292682.1) and cannabichromenic acid synthase (CBCAS; GenBank acc. no. LY658671.1). (a) Protein sequence alignments of THCAS, CBDAS and CBCAS were performed using Clustal Omega and protein domains were annotated using interproscan v.5.41‐78.0 (Sievers et al., 2011; Jones et al., 2014). The p‐cresol methylhydroxylase (PCMH)‐type flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)‐binding domain (residues 77–251, PrositeProfiles: PS51387, InterPro:IPR016166) and berberine and berberine‐like domain (residues 480–538 for THCAS and CBCAS, residues 479–537 for CBDAS, Pfam: PF08031, InterPro: IPR012951) are highlighted in red and black, respectively. The FAD‐binding domain (residues 81–214, Pfam: PF01565, IPR006094) is not shown. (b) THCAS is more similar to CBCAS than CBDAS at the nucleotide and amino acid levels. It is possible that the presence of CBCAS may lead to the production of THCA as a by‐product (McKernan et al., 2020).
