Figure 7.
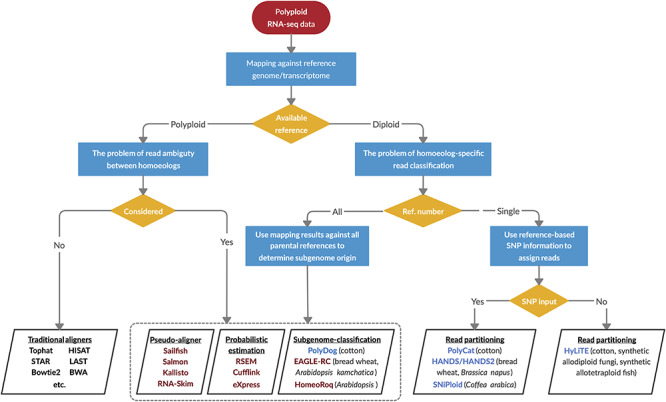
A decision-making diagram to choose the appropriate bioinformatic resources for estimating homoeolog expression levels. When a reference genome or transcriptome is available for the polyploid species, quantification of individual homoeologs is straightforward using the traditional aligners such as TopHat, or the problem of read ambiguity by applying probabilistic estimation methods, pseudo-aligners or subgenome-classification approaches is considered. The latter also applies to the scenario when subgenome references are available from all the diploid progenitors. When the reference is only available for one diploid progenitor, software has been developed for partitioning and quantifying homoeolog-specific reads given the genetic variants such as SNPs between homoeologous sequences. Maroon-colored software, such as RSEM and EAGLE-RC, statistically assigns the subgenome origin for ambiguously mapped reads; blue-colored software such as PolyCat utilizes only unambiguously mapped reads for estimation. The polyploid systems for which they were originally developed are noted in parentheses.
