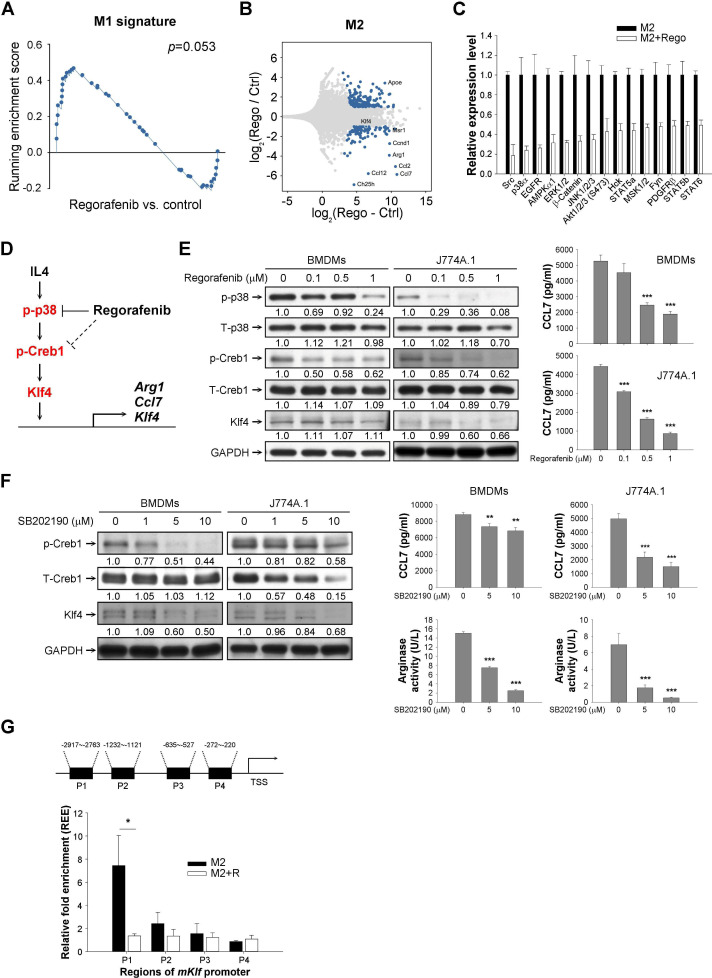
Figure 4.
Regorafenib may regulate macrophage polarization through suppressing p38MAPK-Creb1-Klf4 pathway. (A) Gene-set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of M1 signature in regorafenib-treated or vehicle-treated M2 macrophages derived from bone marrow–derived macrophages (BMDMs). BMDMs were pretreated with regorafenib 1 µM for 1 hour, polarized to M2 phenotype, and total RNA were harvested for RNA-sequencing. (B) Representative genes regulated by regorafenib in M2 BMDMs. Genes with log (fold changes) (logFC) of >1 or <−1 were listed. (C) Inhibition of representative kinases in BMDMs by regorafenib 1 μM (phospho-kinase array). Kinases with ≥50% suppression of phosphorylation were shown. (D) A proposed mechanism by which regorafenib may prevent the M2 polarization of macrophages. (E) Suppression of p38MAPK and the downstream Creb1 phosphorylation and expression of Klf4 and CCL7 by regorafenib in macrophages. (F) Suppression of Creb1 phosphorylation, Klf4/CCL7 expression, and arginase activity in macrophages by the p38MAPK inhibitor SB202190. The number below each band in the western blot indicated the relative intensity of staining signals measured by ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health, https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/). (G) Binding of the transcription factor Creb1 to the predicted binding sites at the Klf4 promoter. Regorafenib (1 µM) significantly suppressed Creb1 binding to Klf4 promoter, particularly the −2917 to −2763 site, in M2 BMDMs. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p <0.001.