FIGURE 4.
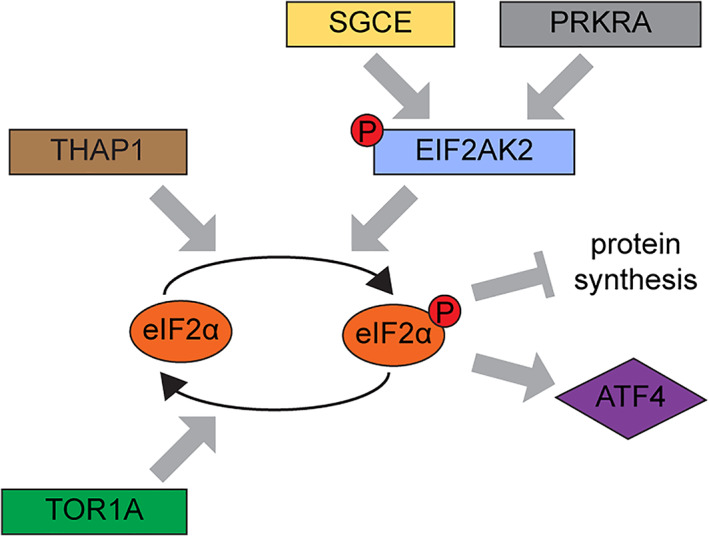
Evidence for dysregulated eIF2α signaling as a shared theme in the pathogenesis of dystonia. Identification of EIF2AK2 variants in this study provides further support for dysregulated eIF2α signaling as a shared pathogenetic theme in dystonia. Evidence for a disturbed integrated stress response (ISR) has been previously reported in other monogenic causes of dystonia, including DYT‐PRKRA, DYT‐TOR1A, DYT‐THAP1, and DYT‐SGCE. Several studies have shown that variants in the PRKRA gene enhanced the susceptibility to endoplasmic reticulum stress leading to heightened EIF2AK2 activation, dysregulation of ISR, and increased apoptosis. 32 , 34 , 35 ISR dysregulation has been reported to play a central role in DYT‐TOR1A. 10 , 11 , 36 THAP1 mutations have been shown to cause dysregulation of the eIF2α signaling pathways in a DYT‐THAP1 mouse model. 12 In a mouse model of DYT‐SGCE, significantly elevated levels of EIF2AK2 transcript are reported, and genes associated with protein translation are among the top downregulated mRNAs. 37 Additionally, rare variants in ATF4—a direct target of eIF2α signaling—have also been reported in cervical dystonia patients. 11 [Color figure can be viewed at www.annalsofneurology.org]
