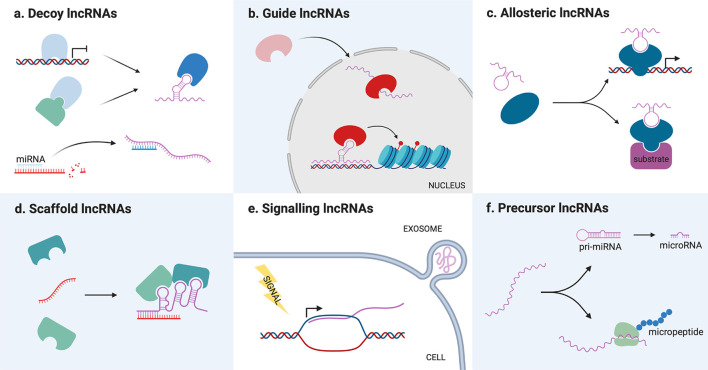
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) different molecular mechanisms. (A) Decoy lncRNAs titrate away proteins or miRNAs from their molecular partners, inhibiting their function. (B) Guide lncRNAs bind protein partners and direct them toward a specific cellular compartment or genomic target. (C) Allosteric lncRNAs interact with transcription factors or enzymes causing structural modifications that modify their activity. (D) Scaffold lncRNAs bind different molecular partners (proteins or RNAs) allowing them to interact or assemble into a complex. (E) Signaling lncRNAs are transcribed following a stimulus for which they act as signal molecules. They can be packed in exosomes and transmitted to other cells. (F) Precursor lncRNAs are processed into miRNAs or translated into functional micropeptides.