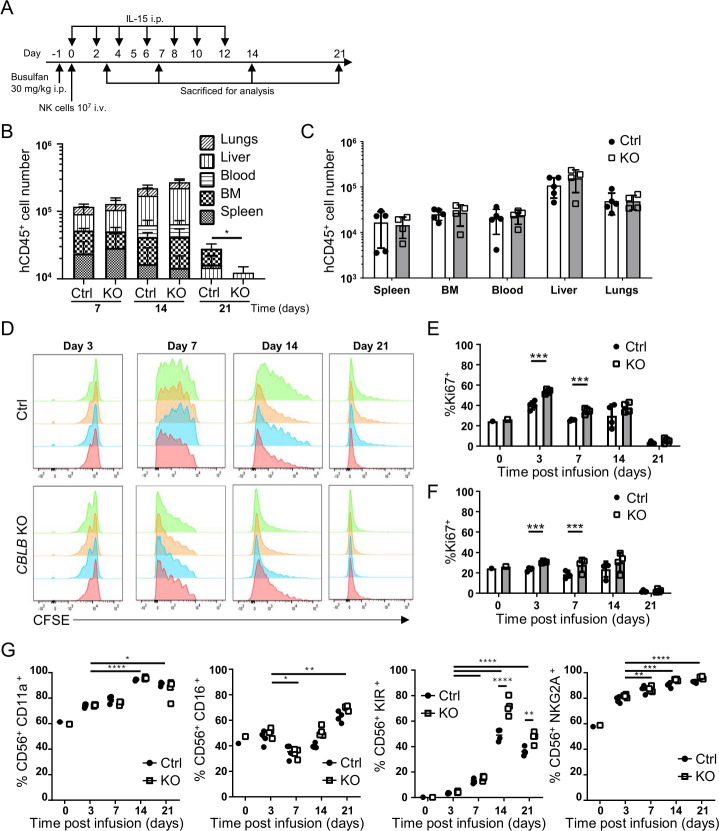
Figure 3.
Biodistribution and persistence of CBLB KO PNK cells in vivo. (A) Schematic of experimental procedures for in vivo biodistribution and proliferation studies. CBLB KO or Ctrl PNK cells were injected intravenously into NSG mice 1 day after intraperitoneal busulfan treatment. rhIL-15 was administered intraperitoneally every 2 days until day 12. Animals were sacrificed on days 3, 7, 14 and 21 for analysis of PNK cells using hCD45 staining (n=4–5). (B) Quantification of hCD45+ cell numbers quantified in blood, BM, liver, lungs and spleen on days 7, 14 and 21 after infusion of Ctrl or CBLB KO PNK cells. (C) Quantification of hCD45+ cells in indicated organs on day 14 after PNK cell infusion, mean±SD (n=5). (D) CFSE-labeled Ctrl or CBLB KO PNK cells were injected intravenously in NSG mice, and animals were sacrificed on days 3, 7, 14 or 21 to analyze CFSE signal on PNK cells. Each histogram represents data from one mouse (n=4). (E, F) Proportion of PNK cells isolated from the liver (E) or the lungs (F), expressing the proliferation marker Ki67. (G) Quantification of indicated NK cell surface receptors on Ctrl or CBLB KO PNK cells after harvested from mice. Day 0 sample represents the preinfusion phenotype. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. BM, bone marrow; CBLB, Casitas B-lineage lymphoma pro-oncogene-b; CFSE, carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester; Ctrl, control; h, human; IL, interleukin; KO, knockout; NK, natural killer; NSG, NOD-scid IL2R gammanull; PNK, placental CD34+ cell-derived NK.