Fig. 3.
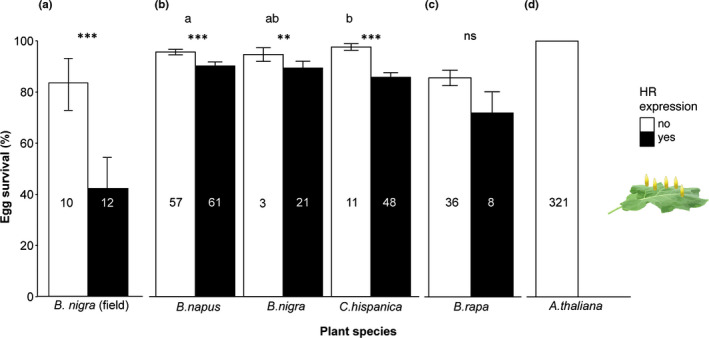
Effect of hypersensitive response (HR)‐like necrosis on survival rates of singly laid Pieris eggs on different plant species. (a) Effect of HR‐like necrosis on egg survival in field conditions. Survey of P. napi and P. rapae eggs on Brassica nigra plants located near the river Rhine in Wageningen (the Netherlands). One to 13 eggs were sampled per plant. (b–d) Effect of HR‐like necrosis on egg survival under glasshouse conditions. Single eggs were separately laid on the leaf without touching each other as shown on the right side. Three experiments were performed with singly laid P. brassicae eggs on different accessions of B. napus, B. nigra, Campe hispanica (b) and B. rapa (c) as well as P. rapae eggs laid on Arabidopsis thaliana (d). Ten single eggs were laid on each plant for experiment (b), five single P. brassicae eggs on each plant for experiment (c) and a single P. rapae egg per plant for (d). If a plant expressed HR‐like necrosis under at least one egg it was counted as HR‐expressing ‘yes’. Numbers in columns represent number of plants tested. Egg survival represents mean ± SE of hatched eggs for each plant. If a plant expressed HR‐like necrosis under at least one egg it was counted as HR‐expressing ‘yes’. Asterisks indicate significant differences in egg survival between plants with or without HR‐like necrosis. Different letters indicate significant differences in egg survival between plant species, without taking HR‐like necrosis into account (GLM; ns, not significant; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).
