Figure 5.
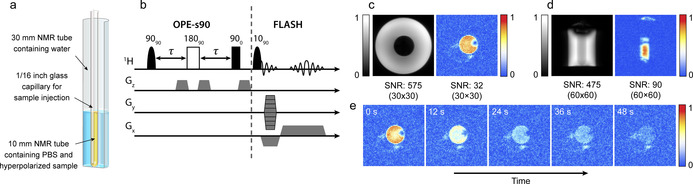
(a) A schematic of the imaging phantom. (b) The pulse sequence used to acquire hyperpolarized 1H images. (c,d) A comparison between the hyperpolarized and thermal equilibrium 1H images, with the hyperpolarized images acquired following the procedure described in the text. (e) A time series of hyperpolarized 1H images. The receiver gain was set to 101 for hyperpolarized image acquisition and 1 for thermal equilibrium image acquisition, which gives a factor of 2 difference in signal‐to‐noise ratio (as discussed in the Supporting Information).
