Fig. 2. TLR4 modulation of calcium-permeable AMPAR currents in hippocampal neuron-only cultures in vitro.
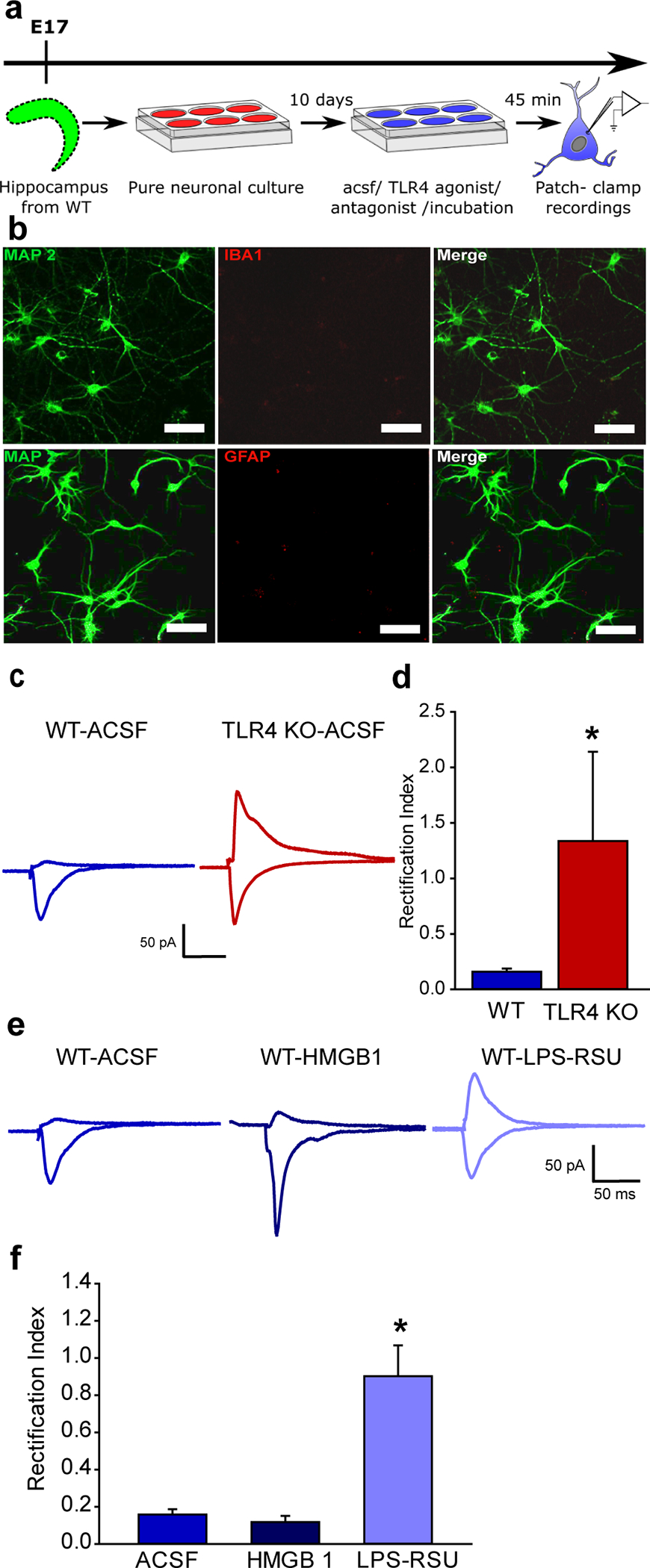
a. Schematic of the experimental paradigm illustrates the timeline for isolation of the hippocampus and maintenance in vitro followed by electrophysiology. b. Representative maximum intensity projection of confocal image stacks from a neuronal culture plated at embryonic day 17 and stained for MAP2 at DIV 12 to reveal neurites. c. Representative traces of AMPAR current recordings in neurons cultured from WT (left) and TLR4−/− mice (right) in response to a 1 mA stimulus to the neuropil. Recordings were obtained from holding potentials of −60 mV and +40 mV as in Fig. 1f. Note the AMPAR current rectification in neurons from WT and symmetric currents in TLR4-/−. d. Summary plot of rectification index measured as the ratio of peak AMPAR current at +40 mV to the peak current at −60 mV. (* indicates p<0.05 by Mann-Whitney test). e. Sample AMPAR current traces recorded in response to neuropil stimulation in WT neuronal cultures. Neurons were held at +40mV and −60 mV to obtain recordings in ACSF (left), TLR4 agonist HMGB1 (middle) and TLR4 antagonist LPS-RSU (right). Note the AMPAR current rectification in the absence of drugs and symmetric currents in LPS-RSU. f. Summary plot of rectification index. * indicates p<0.05 by One Way ANOVA on ranks followed by post-hoc Tukey’s test.
