Fig. 8. Augmenting AMPAR currents increases seizure susceptibility in TLR4 antagonist-treated brain-injured rats.
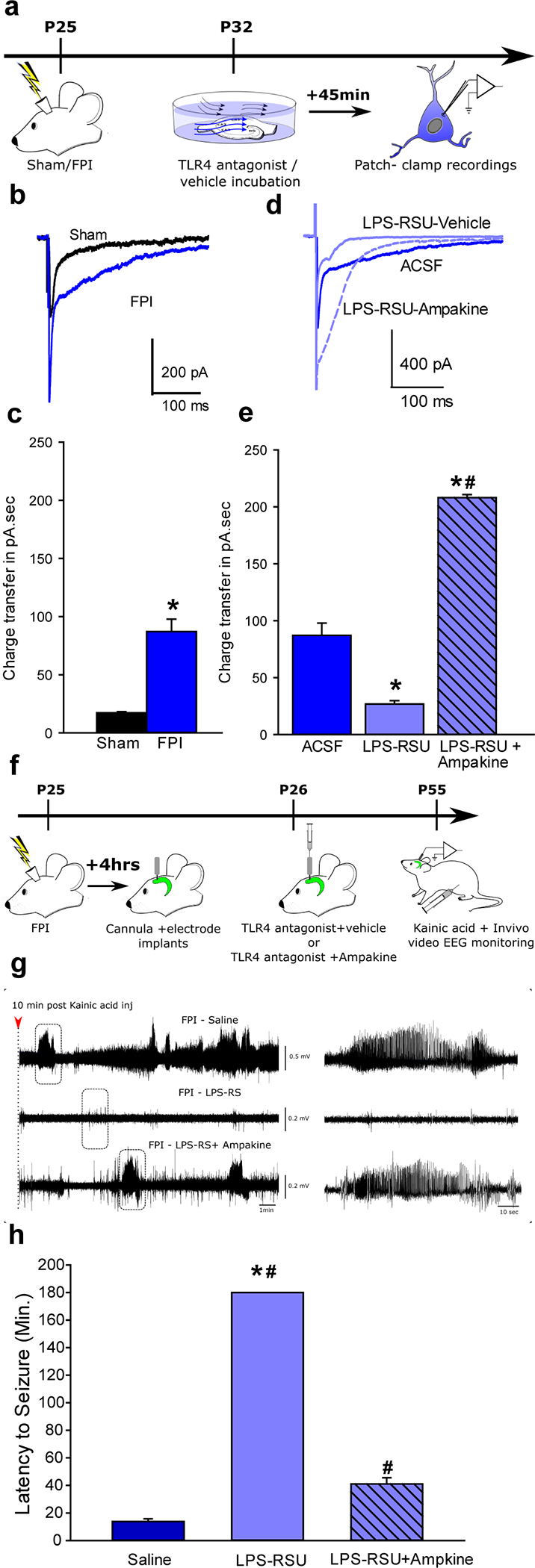
a. Schematic for experiments testing the efficacy of Ampakine to enhance perforant path-evoked AMPAR currents in ex vivo preparations. b. Overlay of afferent evoked AMPAR currents in slices from sham (black) and FPI (blue traces) rats. c. Summary histograms of AMPAR charge transfer in experimental groups. *indicate p<0.05 by Mann Whitney test. d. Overlay of afferent-evoked AMPAR currents in slices from FPI rats incubated in ACSF/saline (dark blue), LPS-RSU and saline (light blue solid line) and LPS-RSU and CX546 (light blue dashed line). e. Summary histograms of AMPAR charge transfer in experimental groups. *indicate p<0.05 by One Way ANOVA on ranks followed by post-hoc Tukey’s test for differences between slices from FPI following different drug incubations. The same data set for FPI-ACSF is used in panels c and e. f. Illustration of treatments and timeline for testing the ability of CX546 to alter seizure susceptibility. g. Sample hippocampal depth electrode recordings in brain injured rats treated with saline or LPS-RSU (2mg/ml) or LPS-RSU (2mg/ml) + CX546 (300μM). EEG recordings obtained 10 minutes after KA (5 mg/kg, i.p) injection shows the early development of seizures in saline treated FPI rats (above), lack of seizure activity in FPI rats treated with LPS-RSU 24 hours after injury (middle) and development of seizure activity in FPI rats treated with CX546and LPS-RSU (lower). Expanded traces in the boxed areas are shown (right panels). h. Summary plot of latency to KA induced seizures. Saline and LPS-RSU data in h were presented in 5b. * indicates p<0.05 from saline and # indicates p<0.05 compared to LPS-RSU by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
