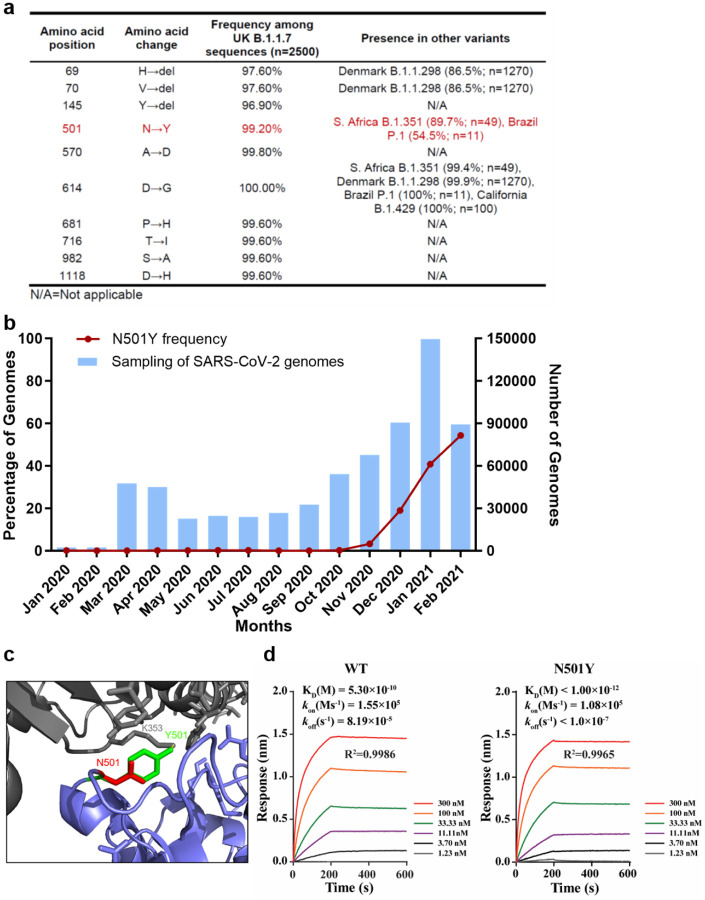
Figure 4. The spike N501Y substitution spread quickly and increases spike protein binding affinity for the human ACE2 receptor.
a, The frequencies of the spike protein amino acid substitutions found among UK B.1.1.7 isolates and other variants. The amino acid substitutions in the UK B.1.1.7 variant refers to the USA_WA1/2020 SARS-CoV-2 sequence (GenBank accession No. MT020880). b, The frequency of the N501Y substitution over time in all genomic SARS-CoV-2 sequences available from the GISAID database worldwide. The blue bars represent the total numbers of SARS-CoV-2 genomes sequenced worldwide. The red line indicates the percentage of N501Y variant in total SARS-CoV-2 genomes. c, The predicted binding site of the N501 and Y501 residues to the human ACE2 receptor. d, The binding affinities of the wt and N501Y mutant to the human ACE2 receptor. Binding affinity-related parameters, including association (Kon), dissociation (Koff), and affinity (KD) are shown. The affinity of ACE2 to the N501Y mutant RBD is below the detection limit and is presented as <10−12.