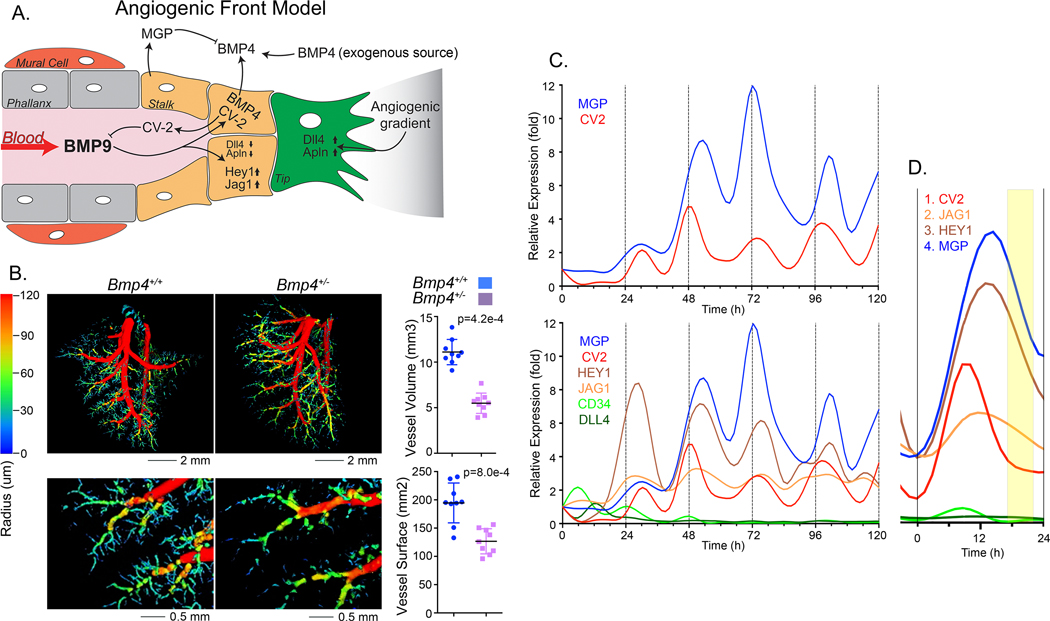
Figure 3: BMP9 triggers expression of stalk cell markers in HPAEC.
(A) Angiogenic front working model: BMP4 is available from exogenous sources or local ECs and induces expression of ALK1 and VEGF. The availability of ALK1 allows signaling by circulating BMP9. BMP9 induces CV2 and MGP that antagonizes BMP9 and BMP4, respectively, and coordinate the actions of the two BMPs. (B) Lung vasculature of mice wild type (Bmp4+/+) mice and heterozygous for Bmp4 gene deletion (Bmp4+/−) mice by micro-CT imaging (left) with quantification of vessel surface and volume (right) (mean±SD; Mann-Whitney test, duplicate imaging). (C) Expression profiles for CV2, MGP, HEY1, JAG1, CD34 and DLL4 in HPAEC treated with BMP9 (10 ng/ml), RNA was collected every 6 hours for up to 120 hours, and expression was determined by qPCR, first normalized to GAPDH and then its own control. Adjusted R2 and p-values from non-linear polynomial regression were as follows: CV2: adjusted R2 0.328, p-value 0.025; MGP: adjusted R2 0.594, p-value 0.001; JAG1: adjusted R2 0.490, p-value 0.010; HEY1: adjusted R2 0.339, p-value 0.022. Representative of 5 replicate experiments. (D) Enlarged view of the second oscillation in panel C.