Figure 8: Effect of MGP deficiency on mouse retinal vasculature (postnatal day 7, P7).
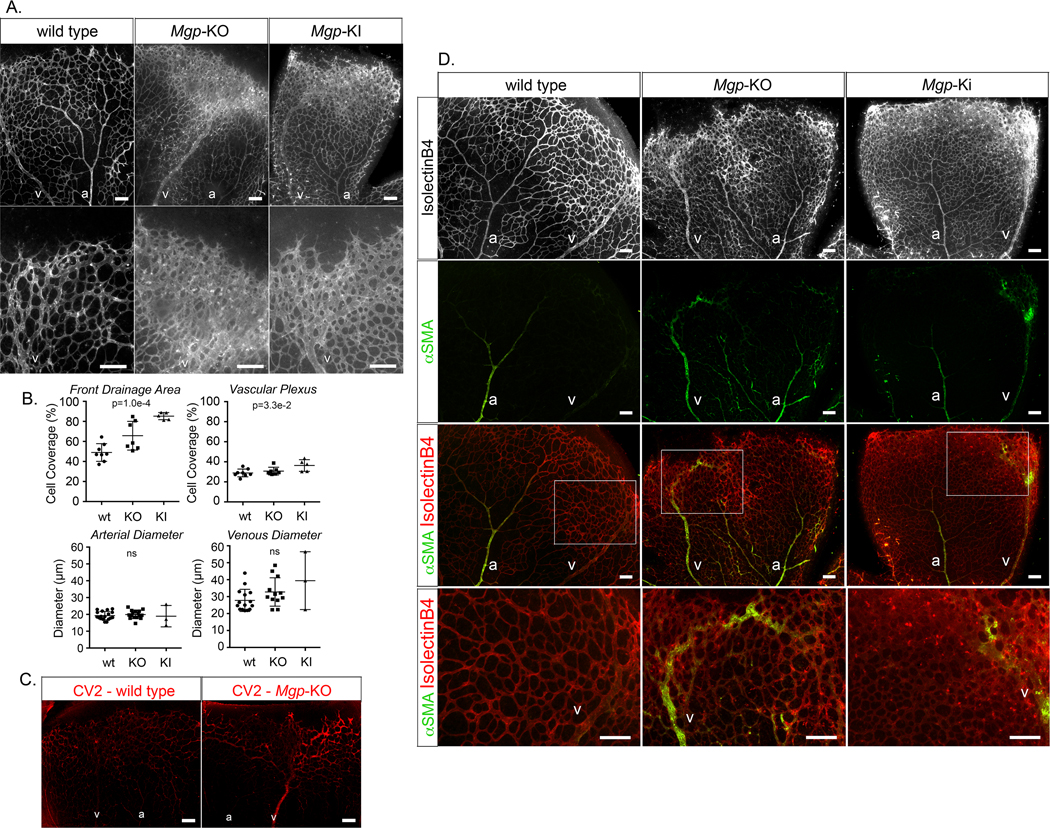
(A) Mouse retinal vasculature from wild type, Mgp-knockout (KO) and Mgp-knockin (KI) mouse stained with Isolectin B4 (IB4) (white). (B) Quantitative analysis of percent cell coverage in the front drainage area and the vascular plexus (top) and arterial and venous diameters (bottom) (mean ± SD, determined from 8 or more retinas for wild type and Mgp-KO, and 3 or 5 retinas for Mgp-KI; Kruskal-Wallis test). (C) Immunofluorescence showing CV2 staining (red) in retina from wild type and Mgp-KO mouse. (D) (Top panels) mouse retinal vasculature from wild type, Mgp-KO and Mgp-KI mouse stained with Isolectin B4 (white). (Middle panels) alpha-smooth muscle actin (aSMA) staining (green) together with IB4 staining (red). (Bottom panels) Enlarged views of the indicated areas.
a; artery, v; vein; all bars, 200 μm; each panel is representative of ≥ 5 replicate staining experiments.
