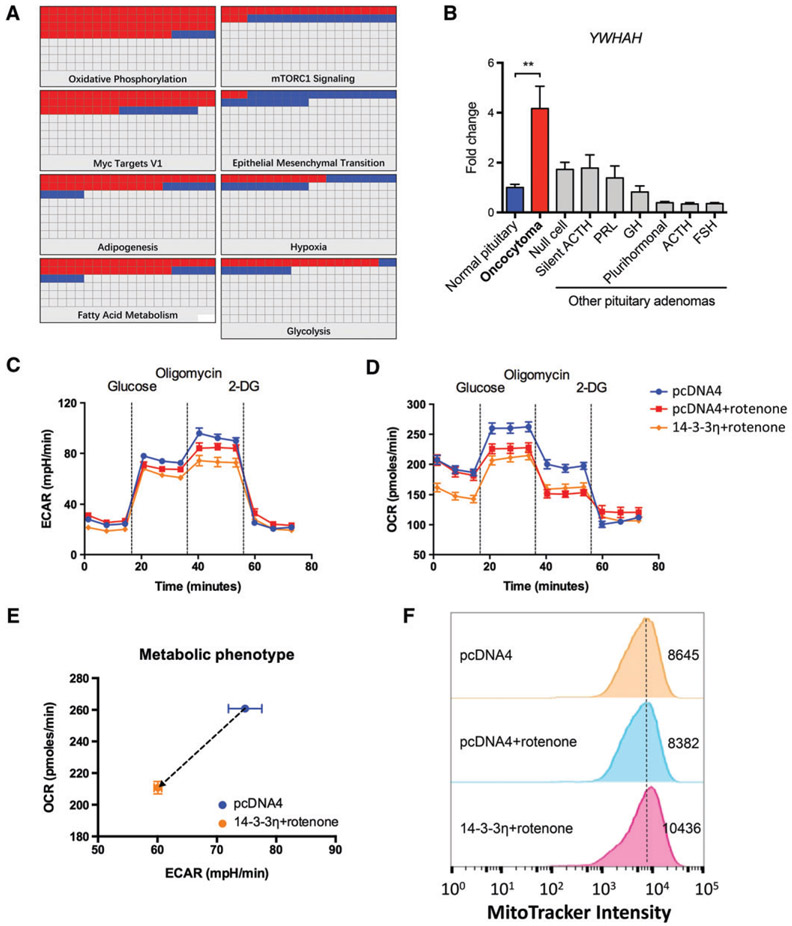
Figure 4.
14-3-3η is a putative inhibitor of glycolysis and is critical for mitochondrial biogenesis. (A) Proteomic study showed significant changes in several signalling pathways, including oxidative phosphorylation, hypoxia, and glycolysis. (B) YWHAH was exclusively overexpressed in oncocytoma; n = 5, n = 10, n = 7, n = 5, n = 7, n = 8, n = 10, n = 5 and n = 10 for normal tissue, oncocytoma, null-cell adenoma, silent adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) adenoma, prolactin (PRL)-secreting adenoma, growth hormone (GH)-secreting adenoma, plurihormonal adenoma, ACTH-secreting adenoma, and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)-secreting adenoma, respectively. (C-E) In the HEK293T model, 14-3-3η transfection inhibited glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration when complex I was inhibited by rotenone (100 nM). (F) Flow cytometry showed that 14-3-3η led to an increased number of mitochondria in the HEK293T cells with pharmacologically induced oxidative phosphorylation dysfunction. **p < 0.01. mTORC1, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1.