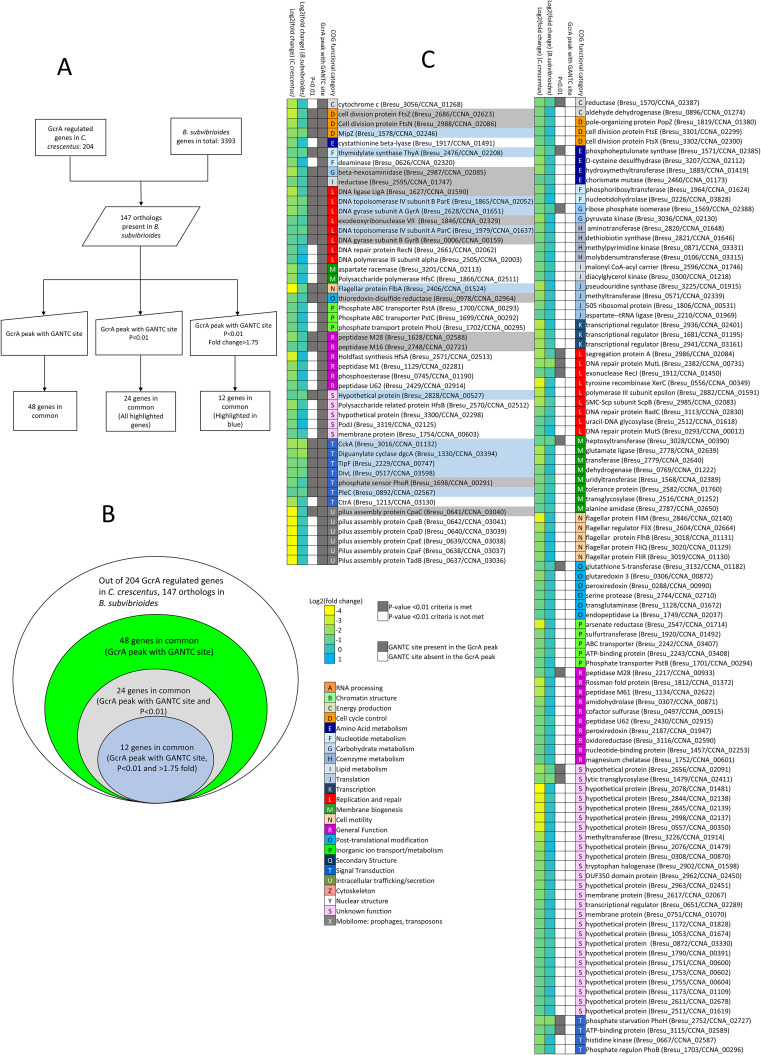
Fig 4. Common genes regulated by GcrA in B. subvibrioides and C. crescentus.
A) Workflow showing the cutoffs used for defining common genes belonging to GcrA regulon in B. subvibrioides and C. crescentus. Out of 204 GcrA regulated genes in C. crescentus, 147 orthologs found in B. subvibrioides. Only few genes were in common despite using different cutoffs to define GcrA regulon in B. subvibrioides. B) Concentric circle diagram showing common genes using different cutoffs. B. subvibrioides has 147 orthologs to the 204 GcrA targets in C. crescentus. Of those 147 genes, only 48 had detectable GcrA peaks (obtained from ChIP-seq data) with GANTC sites. Only 24 of those 48 genes had transcriptional changes meeting a P<0.01 cutoff in the gcrA mutant (all highlighted genes in Fig 4C), and only 12 of those met the >1.75-fold change transcriptional cutoff (highlighted blue in Fig 4C). C) List showing all 147 B. subvibrioides genes orthologous to the 204 members of the published C. crescentus GcrA regulon, sorted by COG functional category. For both left and right, Column 1 and 2 is the heat map showing the magnitude of fold change in log2 scale in C. crescentus gcrA strain (data obtained from [19]) and B. subvibrioides gcrA strain respectively. Column 3 shows genes that met P<0.01 criteria or not in B. subvibrioides (grey—P<0.01 is met, white—P<0.01 is not met). Column 4 shows if those genes have GcrA peaks with GANTC sites within their promoter in B. subvibrioides (grey—GcrA peak with GANTC site present, white—GcrA peak with GANTC site absent). Genes were clustered by COG functional category (Column 5). Orthologs with GcrA peaks containing a GANTC site are shown in the left and orthologs without GcrA peaks containing a GANTC site are shown in the right. Orthologs with GcrA peak and P<0.01 are highlighted (blue and gray). Orthologs with GcrA peak, P<0.01 and >1.75-fold change are shown in highlighted blue.