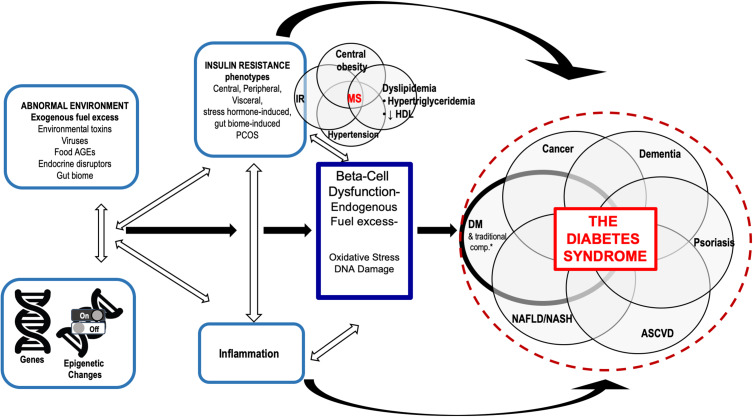
Figure 1.
Overlapping pathophysiologic mechanisms that lead to the diabetes syndrome.
Notes: Insulin resistance, its complications, and other conditions arise from common pathophysiologies. Metabolic syndrome, obesity, and PCOS, etc, can be viewed as phenotypes related to genes and epigenetic changes associated with IR. Insulin resistance along with inflammation increase the risk of β-cell dysfunction as well as the Diabetes Syndrome. *Traditional DM complications include retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy-tissues that do not require insulin to get glucose into cells.
Abbreviations: AGE, advanced glycosylation end products; ASCVD, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; DM, diabetes mellitus; DNA, deoxynucleic acid; HDL, high density lipoprotein; IR, insulin resistance; MS, metabolic syndrome; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; PCOS, polycystic ovary disease.