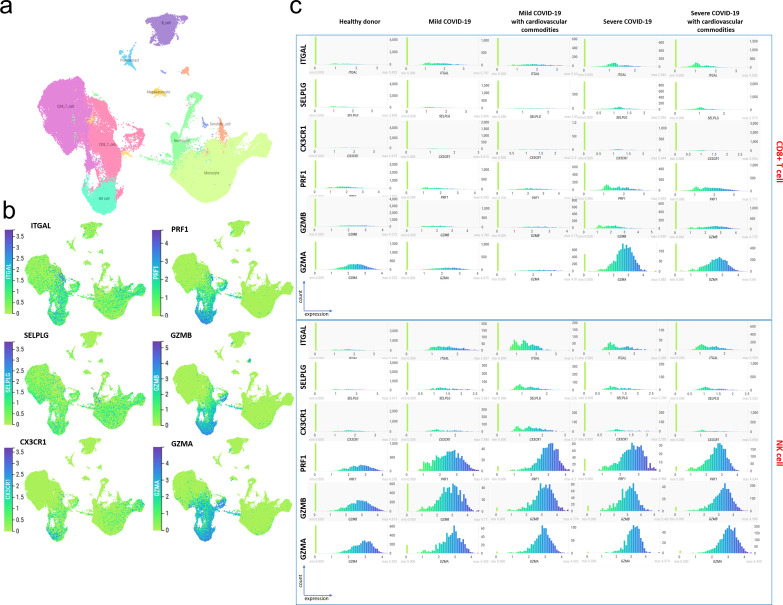
(
a) Single cell transcriptomic dataset published by
Schulte-Schrepping et al., 2020 were re-analyzed using the cellxgene platform hosted by Fastgenomics database (
https://beta.fastgenomics.org/datasets/detail-dataset-952687f71ef34322a850553c4a24e82e#Cellxgene). The samples were annotated as mild (WHO 2–4) or severe (5—7) COVID-19 disease according to the WHO clinical ordinal scale and with or without cardiovascular commodity following publication Table S1 annotations. The UMAP representing immune cell populations compilated from healthy donor (n = 21), mild with (n = 4) or without (n = 4) cardiovascular comorbidity, and severe with (n = 8) or without (n = 2) cardiovascular comorbidity was annotated using the metadata included in the ‘cluster_labels_res.0.4els_res.0.4’ taxonomy. For better clarity, the clusters of the same cell type were pooled together. (
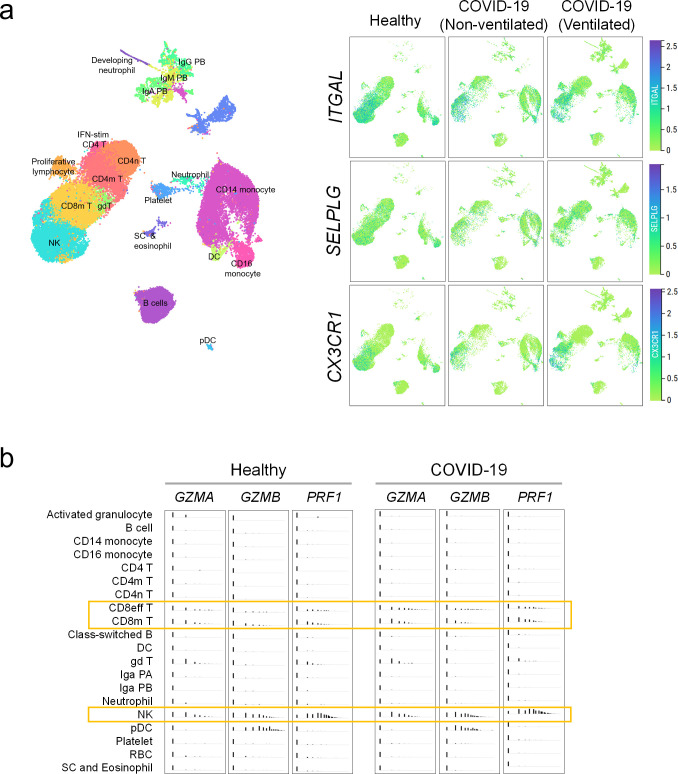
b) Expression of counter receptors (
ITGAL, SELPLG, and
CX3CR1) and cytotoxicity-associated genes (
PFR1, GMZB and
GMZA) across immune cell population. Both set of genes are mainly expressed by CD8
+ and NK cells and to some extent monocyte. (
c) Distribution of the expression of counter receptors and cytotoxicity associated genes in CD8
+ cell (top) and NK (bottom) in mild and severe COVID-19 samples with or without cardiovascular comorbidity. Compared to healthy donors, mild and severe COVID-19 samples have a higher proportion of NK or both CD8
+ and NK cells expressing counter receptors and cytotoxicity-associated genes, respectively. No difference can be observed in presence or absence of cardiovascular comorbidity.