Fig. 1.
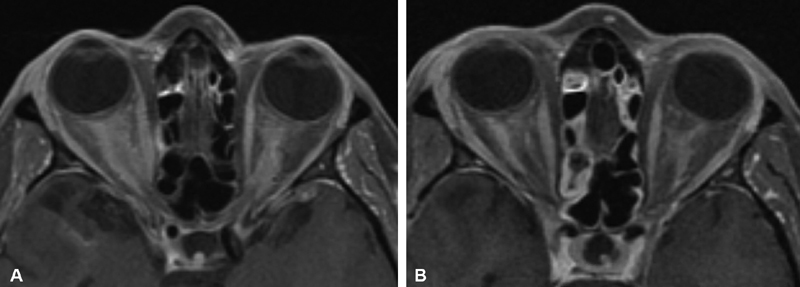
( A ) Axial T1-weighted, postcontrast MRI from a patient who presented with progressive bilateral visual loss over 2 years, and was found to have bilateral optic nerve edema and bilateral optic disc shunt vessels on exam. Symptoms were not responsive to a course of corticosteroids. ACE level and Gallium studies were normal without evidence of sarcoid. Right optic nerve biopsy via superior medial orbitotomy was nondiagnostic but showed no evidence of inflammation nor granuloma. The diagnosis of bilateral optic nerve sheath meningioma was therefore presumptive, and treated with 5,040 cGY IMRT radiation in 28 fractions of 1.8 Gy with significant improvement in vision after treatment. ( B ) 3 years later, with stable improved bilateral vision, axial T1-weighted, postcontrast MRI showed persistence of bilateral enhancement supporting the presumptive diagnosis of bilateral pONSM. ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme; IMRT, intensity-modulated radiotherapy; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; pONSM, primary optic nerve sheath meningioma.
