Fig. 13.
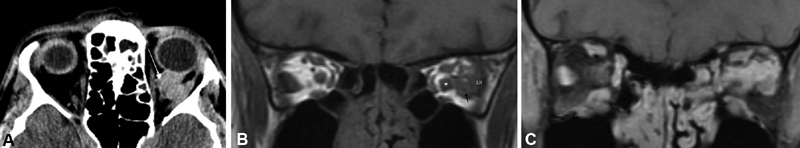
( A ) Noncontrast orbital axial CT image of the same lesion reveals scattered calcifications (arrow indicates large calcification) in the left retrobulbar space at the edge of the lesion, which may be seen in meningioma as well as venous orbital lesions such as this. ( B ) Noncontrast coronal T1 image without fat suppression demonstrates a left-sided lesion (arrow) in the posterior orbit distinct from the optic nerve, blending with the left lateral rectus (LR). In other areas of the orbit it was more difficult to separate the lesion from the optic nerve sheath complex. In this non-fat suppressed image, the bright signal of the fat serves to help delineate the nerve (asterisk) which is of normal size, separate from the lesion. ( C ) Coronal T1-weighted, postcontrast MRI images demonstrate a diffuse enhancing lesion extending from the optic nerve sheath complex, infiltrating the orbit between the nerve, superior rectus levator complex and lateral rectus. It would be too difficult to differentiate this vascular malformation from an ONSM on this image. CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; ONSM, optic nerve sheath meningioma.
